RIG-I like receptor sensing of host RNAs facilitates the cell-intrinsic immune response to KSHV infection
- PMID: 30451863
- PMCID: PMC6242832
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07314-7
RIG-I like receptor sensing of host RNAs facilitates the cell-intrinsic immune response to KSHV infection
Abstract
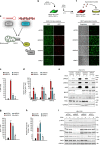
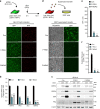
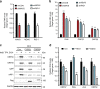
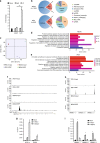
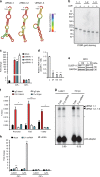
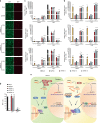
The RIG-I like receptors (RLRs) RIG-I and MDA5 are cytosolic RNA helicases best characterized as restriction factors for RNA viruses. However, evidence suggests RLRs participate in innate immune recognition of other pathogens, including DNA viruses. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is a human gammaherpesvirus and the etiological agent of Kaposi's sarcoma and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). Here, we demonstrate that RLRs restrict KSHV lytic reactivation and we demonstrate that restriction is facilitated by the recognition of host-derived RNAs. Misprocessed noncoding RNAs represent an abundant class of RIG-I substrates, and biochemical characterizations reveal that an infection-dependent reduction in the cellular triphosphatase DUSP11 results in an accumulation of select triphosphorylated noncoding RNAs, enabling their recognition by RIG-I. These findings reveal an intricate relationship between RNA processing and innate immunity, and demonstrate that an antiviral innate immune response can be elicited by the sensing of misprocessed cellular RNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RIG-I Detects Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Transcripts in a RNA Polymerase III-Independent Manner.mBio. 2018 Jul 3;9(4):e00823-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00823-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29970461 Free PMC article.
-
Oncostatin M induces RIG-I and MDA5 expression and enhances the double-stranded RNA response in fibroblasts.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Nov;21(11):3087-3099. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13221. Epub 2017 May 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28560754 Free PMC article.
-
A RIG-I-like receptor directs antiviral responses to a bunyavirus and is antagonized by virus-induced blockade of TRIM25-mediated ubiquitination.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 10;295(28):9691-9711. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013973. Epub 2020 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32471869 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of RIG-I-Like Receptors and Insights into Viral RNA Sensing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1172:157-188. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9367-9_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31628656 Review.
-
RIG-I-Like Receptors and Type I Interferonopathies.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017 May;37(5):207-213. doi: 10.1089/jir.2016.0095. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2017. PMID: 28475461 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vault RNAs: hidden gems in RNA and protein regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(4):1487-1499. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03675-9. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33063126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinoic Acid Inducible Gene I and Protein Kinase R, but Not Stress Granules, Mediate the Proinflammatory Response to Yellow Fever Virus.J Virol. 2020 Oct 27;94(22):e00403-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00403-20. Print 2020 Oct 27. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32878892 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic caspases suppress an MDA5-driven IFN response during productive replication of human papillomavirus type 31.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jul 19;119(29):e2200206119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200206119. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35858339 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19: A novel holistic systems biology approach to predict its molecular mechanisms (in vitro) and repurpose drugs.Daru. 2023 Dec;31(2):155-171. doi: 10.1007/s40199-023-00471-1. Epub 2023 Aug 19. Daru. 2023. PMID: 37597114 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic RNA sensors and their interplay with RNA-binding partners in innate antiviral response: theme and variations.RNA. 2022 Apr;28(4):449-477. doi: 10.1261/rna.079016.121. Epub 2022 Jan 14. RNA. 2022. PMID: 35031583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

