Exosomes and Exosome-Inspired Vesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery
- PMID: 30404188
- PMCID: PMC6321407
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040218
Exosomes and Exosome-Inspired Vesicles for Targeted Drug Delivery
Abstract
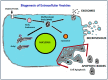
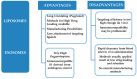
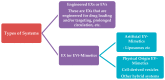
The similarities between exosomes and liposomes, together with the high organotropism of several types of exosomes, have recently prompted the development of engineered-exosomes or exosome-mimetics, which may be artificial (liposomal) or cell-derived vesicles, as advanced platforms for targeted drug delivery. Here, we provide the current state-of-the-art of using exosome or exosome-inspired systems for drug delivery. We review the various approaches investigated and the shortcomings of each approach. Finally the challenges which have been identified to date in this field are summarized.
Keywords: bioinspired systems; drug delivery; drug targeting; engineered systems; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; liposomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advances in Exosome-Based Drug Delivery and Tumor Targeting: From Tissue Distribution to Intracellular Fate.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Nov 24;15:9355-9371. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S281890. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33262592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-like systems: Nanotechnology to overcome challenges for targeted cancer therapies.Cancer Lett. 2023 May 1;561:216151. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216151. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37001751 Review.
-
Exosome mimetics: a novel class of drug delivery systems.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1525-41. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S29661. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22619510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Jun;174:63-78. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.020. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28202367 Review.
-
A Novel Strategy to Increase the Yield of Exosomes (Extracellular Vesicles) for an Expansion of Basic Research.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(5):733-742. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00919. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29709910
Cited by
-
Proinflammatory macrophage-derived microvesicles exhibit tumor tropism dependent on CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis and promote drug delivery via SNARE-mediated membrane fusion.Theranostics. 2020 May 17;10(15):6581-6598. doi: 10.7150/thno.45528. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32550891 Free PMC article.
-
The Mystery of Red Blood Cells Extracellular Vesicles in Sleep Apnea with Metabolic Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4301. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094301. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Affecting Extracellular Vesicles Based Drug Delivery Systems.Molecules. 2021 Mar 11;26(6):1544. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061544. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33799765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formulation and evaluation of atovaquone-loaded macrophage-derived exosomes against Toxoplasma gondii: in vitro and in vivo assessment.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jan 11;12(1):e0308023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03080-23. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38014940 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomes or Extracellular Vesicles: A Comprehensive Comparison of Both Lipid Bilayer Vesicles for Pulmonary Drug Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jan 7;15(2):318. doi: 10.3390/polym15020318. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679199 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

