Nanoparticles That Deliver RNA to Bone Marrow Identified by in Vivo Directed Evolution
- PMID: 30394729
- PMCID: PMC6556374
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b08976
Nanoparticles That Deliver RNA to Bone Marrow Identified by in Vivo Directed Evolution
Abstract
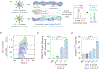
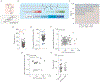
Bone marrow endothelial cells (BMECs) regulate their microenvironment, which includes hematopoietic stem cells. This makes BMECs an important target cell type for siRNA or gene editing (e.g., CRISPR) therapies. However, siRNA and sgRNA have not been delivered to BMECs using systemically administered nanoparticles. Given that in vitro nanoparticle screens have not identified nanoparticles with BMEC tropism, we developed a system to quantify how >100 different nanoparticles deliver siRNA in a single mouse. This is the first barcoding system capable of quantifying functional cytosolic siRNA delivery (where the siRNA drug is active), distinguishing it from in vivo screens that quantify biodistribution (where the siRNA drug went). Combining this approach with bioinformatics, we performed in vivo directed evolution, and identified BM1, a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) that delivers siRNA and sgRNA to BMECs. Interestingly, chemical analysis revealed BMEC tropism was not related to LNP size; tropism changed with the structure of poly(ethylene glycol), as well as the presence of cholesterol. These results suggest that significant changes to vascular targeting can be imparted to a LNP by making simple changes to its chemical composition, rather than using active targeting ligands. BM1 is the first nanoparticle to efficiently deliver siRNA and sgRNA to BMECs in vivo, demonstrating that this functional in vivo screen can identify nanoparticles with novel tropism in vivo. More generally, in vivo screening may help reveal the complex relationship between nanoparticle structure and tropism, thereby helping scientists understand how simple chemical changes control nanoparticle targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
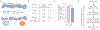
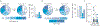

Similar articles
-
Analyzing 2000 in Vivo Drug Delivery Data Points Reveals Cholesterol Structure Impacts Nanoparticle Delivery.ACS Nano. 2018 Aug 28;12(8):8341-8349. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03640. Epub 2018 Jul 20. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 30016076 Free PMC article.
-
Constrained Nanoparticles Deliver siRNA and sgRNA to T Cells In Vivo without Targeting Ligands.Adv Mater. 2019 Oct;31(41):e1902251. doi: 10.1002/adma.201902251. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31465135 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 16;115(42):E9944-E9952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811276115. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30275336 Free PMC article.
-
[Development of siRNA Delivery Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment with a New Functional Device].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(11):1357-1363. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.19-00150. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 31685731 Review. Japanese.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
Cited by
-
Tuning Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery to Extrahepatic Organs.Adv Mater. 2024 Nov;36(44):e2401445. doi: 10.1002/adma.202401445. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 39233550 Review.
-
Effect of Graphene Family Materials on Multiple Myeloma and Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Cell Lines.Materials (Basel). 2020 Aug 3;13(15):3420. doi: 10.3390/ma13153420. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32756412 Free PMC article.
-
Using Large Datasets to Understand Nanotechnology.Adv Mater. 2019 Oct;31(43):e1902798. doi: 10.1002/adma.201902798. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 31429126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction of Beta-Thalassemia IVS-II-654 Mutation in a Mouse Model Using Prime Editing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5948. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115948. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682629 Free PMC article.
-
Biomaterials by design: Harnessing data for future development.Mater Today Bio. 2021 Nov 23;12:100165. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100165. eCollection 2021 Sep. Mater Today Bio. 2021. PMID: 34877520 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Semple SC; Akinc A; Chen J; Sandhu AP; Mui BL; Cho CK; Sah DW; Stebbing D; Crosley EJ; Yaworski E; Hafez IM; Dorkin JR; Qin J; Lam K; Rajeev KG; Wong KF; Jeffs LB; Nechev L; Eisenhardt ML; Jayaraman M; Kazem M; Maier MA; Srinivasulu M; Weinstein MJ; Chen Q; Alvarez R; Barros SA; De S; Klimuk SK; Borland T; Kosovrasti V; Cantley WL; Tam YK; Manoharan M; Ciufolini MA; Tracy MA; de Fougerolles A; MacLachlan I; Cullis PR; Madden TD; Hope MJ, Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat Biotechnol 2010, 28 (2), 172–6. - PubMed
-
- Love KT; Mahon KP; Levins CG; Whitehead KA; Querbes W; Dorkin JR; Qin J; Cantley W; Qin LL; Racie T; Frank-Kamenetsky M; Yip KN; Alvarez R; Sah DW; de Fougerolles A; Fitzgerald K; Koteliansky V; Akinc A; Langer R; Anderson DG, Lipid-like materials for low-dose, in vivo gene silencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107 (5), 1864–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dong Y; Love KT; Dorkin JR; Sirirungruang S; Zhang Y; Chen D; Bogorad RL; Yin H; Chen Y; Vegas AJ; Alabi CA; Sahay G; Olejnik KT; Wang W; Schroeder A; Lytton-Jean AK; Siegwart DJ; Akinc A; Barnes C; Barros SA; Carioto M; Fitzgerald K; Hettinger J; Kumar V; Novobrantseva TI; Qin J; Querbes W; Koteliansky V; Langer R; Anderson DG, Lipopeptide nanoparticles for potent and selective siRNA delivery in rodents and nonhuman primates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2014, 111 (11), 3955–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dahlman JE; Barnes C; Khan OF; Thiriot A; Jhunjunwala S; Shaw TE; Xing Y; Sager HB; Sahay G; Speciner L; Bader A; Bogorad RL; Yin H; Racie T; Dong Y; Jiang S; Seedorf D; Dave A; Singh Sandhu K; Webber MJ; Novobrantseva T; Ruda VM; Lytton-JeanAbigail KR; Levins CG; Kalish B; Mudge DK; Perez M; Abezgauz L; Dutta P; Smith L; Charisse K; Kieran MW; Fitzgerald K; Nahrendorf M; Danino D; Tuder RM; von Andrian UH; Akinc A; Panigrahy D; Schroeder A; Koteliansky V; Langer R; Anderson DG, In vivo endothelial siRNA delivery using polymeric nanoparticles with low molecular weight. Nat Nano 2014, 9 (8), 648–655. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Novobrantseva TI; Borodovsky A; Wong J; Klebanov B; Zafari M; Yucius K; Querbes W; Ge P; Ruda VM; Milstein S; Speciner L; Duncan R; Barros S; Basha G; Cullis P; Akinc A; Donahoe JS; Narayanannair Jayaprakash K; Jayaraman M; Bogorad RL; Love K; Whitehead K; Levins C; Manoharan M; Swirski FK; Weissleder R; Langer R; Anderson DG; de Fougerolles A; Nahrendorf M; Koteliansky V, Systemic RNAi-mediated Gene Silencing in Nonhuman Primate and Rodent Myeloid Cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e4. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

