COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer
- PMID: 30371878
- PMCID: PMC6323903
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky1015
COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer
Abstract
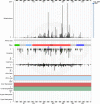
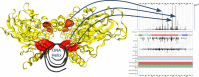
COSMIC, the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer (https://cancer.sanger.ac.uk) is the most detailed and comprehensive resource for exploring the effect of somatic mutations in human cancer. The latest release, COSMIC v86 (August 2018), includes almost 6 million coding mutations across 1.4 million tumour samples, curated from over 26 000 publications. In addition to coding mutations, COSMIC covers all the genetic mechanisms by which somatic mutations promote cancer, including non-coding mutations, gene fusions, copy-number variants and drug-resistance mutations. COSMIC is primarily hand-curated, ensuring quality, accuracy and descriptive data capture. Building on our manual curation processes, we are introducing new initiatives that allow us to prioritize key genes and diseases, and to react more quickly and comprehensively to new findings in the literature. Alongside improvements to the public website and data-download systems, new functionality in COSMIC-3D allows exploration of mutations within three-dimensional protein structures, their protein structural and functional impacts, and implications for druggability. In parallel with COSMIC's deep and broad variant coverage, the Cancer Gene Census (CGC) describes a curated catalogue of genes driving every form of human cancer. Currently describing 719 genes, the CGC has recently introduced functional descriptions of how each gene drives disease, summarized into the 10 cancer Hallmarks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COSMIC (the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer): a resource to investigate acquired mutations in human cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D652-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp995. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19906727 Free PMC article.
-
COSMIC: exploring the world's knowledge of somatic mutations in human cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D805-11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1075. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25355519 Free PMC article.
-
COSMIC: somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jan 4;45(D1):D777-D783. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1121. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27899578 Free PMC article.
-
The COSMIC Cancer Gene Census: describing genetic dysfunction across all human cancers.Nat Rev Cancer. 2018 Nov;18(11):696-705. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0060-1. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30293088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combinatorial patterns of somatic gene mutations in cancer.FASEB J. 2008 Aug;22(8):2605-22. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-108985. Epub 2008 Apr 23. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 18434431 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemoproteogenomic stratification of the missense variant cysteinome.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 28;15(1):9284. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53520-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39468056 Free PMC article.
-
Helical ultrastructure of the metalloprotease meprin α in complex with a small molecule inhibitor.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 19;13(1):6178. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33893-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36261433 Free PMC article.
-
A-to-I RNA Editing in Cancer: From Evaluating the Editing Level to Exploring the Editing Effects.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 11;10:632187. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.632187. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33643923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immuno-oncologic profiling of pediatric brain tumors reveals major clinical significance of the tumor immune microenvironment.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 10;15(1):5790. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49595-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38987542 Free PMC article.
-
AID in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Induction and Action During Disease Progression.Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:634383. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.634383. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collins F.S., Barker A.D.. Mapping the cancer genome. Pinpointing the genes involved in cancer will help chart a new course across the complex landscape of human malignancies. Sci. Am. 2007; 296:50–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

