Epithelial Cells Attenuate Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Monocyte-Derived Macrophage-Like Cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 30356420
- PMCID: PMC6178170
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/3685948
Epithelial Cells Attenuate Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Monocyte-Derived Macrophage-Like Cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Epithelial Cells Attenuate Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Monocyte-Derived Macrophage-Like Cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway".Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Mar 13;2021:3710790. doi: 10.1155/2021/3710790. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33814978 Free PMC article.
Abstract
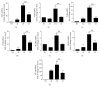
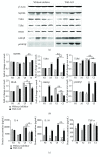
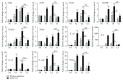
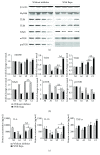
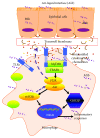
Both alveolar macrophages (AMs) and alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) are main targets of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis (Mtb)). Intercellular communications between mucosal AECs and AMs have important implications in cellular responses to exogenous insults. However, molecular mechanisms underpinning interactions responding to Mtb remain largely unknown. In this study, impacts of AECs on Toll-like receptor- (TLR-) mediated inflammatory responses of AMs to Mtb virulent strain H37Rv were interrogated using an air-liquid interface (ALI) coculture model of epithelial A549 cells and U937 monocyte-derived macrophage-like cells. Results showed that Mtb-activated TLR-mediated inflammatory responses in U937 cells were significantly alleviated when A549 cells were coinfected with H37Rv, in comparison with the infection of U937 cells alone. Mechanistically, PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling was involved in the epithelial cell-modulated Mtb-activated TLR signaling. The epithelial cell-attenuated TLR signaling in U937s could be reversed by PI3K inhibitor LY294002 and mTOR inhibitor rapamycin, but not glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibitor LiCl, suggesting that the epithelially modulated-TLR signaling in macrophages was in part caused by inhibiting the TLR-triggered PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Together, this study demonstrates that mucosal AEC-derived signals play an important role in modulating inflammatory responses of AMs to Mtb, which thus also offers an insight into cellular communications between AECs and AMs to Mtb infections.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR mitigates compensatory AKT activation and improves tamoxifen response in breast cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Oct;11(10):1269-78. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0212. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23814023
-
The involvement of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/GSK3β signaling pathways in the antidepressant-like effect of AZD6765.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Nov;198:173020. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.173020. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32861641
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits dexamethasone-induced proteolysis in cultured L6 myotubes through PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent mechanisms.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;37(10):2207-16. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.04.008. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15927518
-
Zinc enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in Caco-2 cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 May;43:18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 31. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28193579
-
TLR/mTOR inflammatory signaling pathway: novel insight for the treatment of schizophrenia.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;102(3):150-160. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2023-0107. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37955633 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and role of differentially expressed genes/proteins between pulmonary tuberculosis patients and controls across lung tissues and blood samples.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jul;12(7):e1350. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1350. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39023413 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Akt Activator SC79 on Human M0 Macrophage Phagocytosis and Cytokine Production.Cells. 2024 May 24;13(11):902. doi: 10.3390/cells13110902. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891035 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum to "Epithelial Cells Attenuate Toll-Like Receptor-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Monocyte-Derived Macrophage-Like Cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Modulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway".Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Mar 13;2021:3710790. doi: 10.1155/2021/3710790. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 33814978 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative genomics of the mammalian alveolar macrophage response to intracellular mycobacteria.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 12;22(1):343. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07643-w. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33980141 Free PMC article.
-
AKT Isoforms in Macrophage Activation, Polarization, and Survival.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022;436:165-196. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-06566-8_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36243844
References
-
- Chuquimia O. D., Petursdottir D. H., Periolo N., Fernández C. Alveolar epithelial cells are critical in protection of the respiratory tract by secretion of factors able to modulate the activity of pulmonary macrophages and directly control bacterial growth. Infection and Immunity. 2013;81(1):381–389. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00950-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chuquimia O. D., Petursdottir D. H., Rahman M. J., Hartl K., Singh M., Fernández C. The role of alveolar epithelial cells in initiating and shaping pulmonary immune responses: communication between innate and adaptive immune systems. PLoS One. 2012;7(2, article e32125) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032125. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

