Circulating vitamin D level and mortality in prostate cancer patients: a dose-response meta-analysis
- PMID: 30352424
- PMCID: PMC6240137
- DOI: 10.1530/EC-18-0283
Circulating vitamin D level and mortality in prostate cancer patients: a dose-response meta-analysis
Abstract
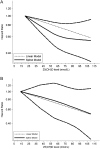
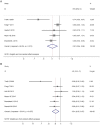
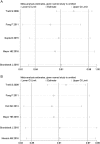
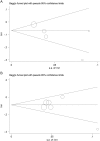
Previous studies investigating the association of circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D level with prognosis of prostate cancer yielded controversial results. We conducted a dose-response meta-analysis to elucidate the relationship. PubMed and EMBASE were searched for eligible studies up to July 15, 2018. We performed a dose-response meta-analysis using random-effect model to calculate the summary hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CI of mortality in patients with prostate cancer. Seven eligible cohort studies with 7808 participants were included. The results indicated that higher vitamin D level could reduce the risk of death among prostate cancer patients. The summary HR of prostate cancer-specific mortality correlated with an increment of every 20 nmol/L in circulating vitamin D level was 0.91, with 95% CI 0.87-0.97, P = 0.002. The HR for all-cause mortality with the increase of 20 nmol/L vitamin D was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.84-0.98, P = 0.01). Sensitivity analysis suggested the pooled HRs were stable and not obviously changed by any single study. No evidence of publications bias was observed. This meta-analysis suggested that higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D level was associated with a reduction of mortality in prostate cancer patients and vitamin D is an important protective factor in the progression and prognosis of prostate cancer.
Keywords: meta-analysis; mortality; prostate cancer; vitamin D.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating vitamin D concentration and risk of prostate cancer: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018 Jan 9;14:95-104. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S149325. eCollection 2018. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018. PMID: 29386901 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Vitamin D Level and Risk of Sudden Cardiac Death and Cardiovascular Mortality: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies.J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Aug 21;38(33):e260. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e260. J Korean Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37605499 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of lung cancer: a dose-response meta-analysis.Cancer Causes Control. 2015 Dec;26(12):1719-28. doi: 10.1007/s10552-015-0665-6. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Cancer Causes Control. 2015. PMID: 26358829 Review.
-
Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and prognosis of lung cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Bull Cancer. 2017 Jul-Aug;104(7-8):675-682. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Bull Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28587766 Review.
-
Body mass index and mortality in prostate cancer patients: a dose-response meta-analysis.Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016 Jun;19(2):122-31. doi: 10.1038/pcan.2015.64. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2016. PMID: 26754262 Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuin 5 regulates the proliferation, invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells through acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase 1.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(23):14039-14049. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16016. Epub 2020 Oct 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33103371 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Factors and Supplements Influencing Prostate Specific-Antigen (PSA) Concentrations in Men with Prostate Cancer and Increased Cancer Risk: An Evidence Analysis Review Based on Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 29;12(10):2985. doi: 10.3390/nu12102985. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33003518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of total cancer incidence and mortality: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2022 Oct 28;8(11):e11290. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11290. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36345522 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Factors and Prostate Cancer Development, Progression, and Reduction.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 3;13(2):496. doi: 10.3390/nu13020496. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33546190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D-Induced Molecular Mechanisms to Potentiate Cancer Therapy and to Reverse Drug-Resistance in Cancer Cells.Nutrients. 2020 Jun 17;12(6):1798. doi: 10.3390/nu12061798. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32560347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diaz GD, Paraskeva C, Thomas MG, Binderup L, Hague A. Apoptosis is induced by the active metabolite of vitamin D3 and its analogue EB1089 in colorectal adenoma and carcinoma cells: possible implications for prevention and therapy. Cancer Research 2000. 60 2304–2312. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

