Polyphyllin I Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Suppressing the Inflammation Response in Macrophages Through the NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 30319603
- PMCID: PMC6170622
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02091
Polyphyllin I Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis by Suppressing the Inflammation Response in Macrophages Through the NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
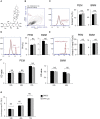
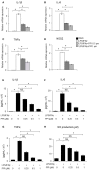
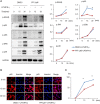
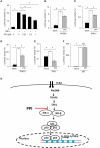
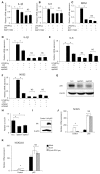
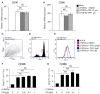
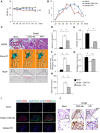
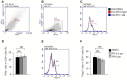
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder, characterized by an increased number of M1-like macrophages in the joints. Polyphyllin I (PPI), one of the main components in the Rhizoma of Paris polyphyllin, displays a selective inhibitory effect on various tumor cells. Here we sought to investigate the anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects and mechanisms of PPI on macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Materials and Methods:In vitro, primary bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) and peritoneal elucidated macrophages (PEMs) were stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and Interferon (IFN)-γ and then treated with PPI. We determined the degree of activation of IKKα/β and p65, two key mediators of the NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway, by measuring their phosphorylated forms by Western blot. The p65 nuclear localization was detected by immunofluorescent staining. Further, a NF-κB-linked luciferase reporter plasmid, as well as those expressing key mediators of the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway, such as myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MYD88), interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) associated kinase (IRAK)-1, TNF receptor associated factors (TRAF)-6, Transforming growth factor-b-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and p65, were used to identify the mechanism by which PPI achieves its inhibitory effects on macrophage-mediated inflammation. Moreover, a NF-κB inhibitor, p65-targeted siRNAs, and a p65 plasmid were further used to validate the anti-inflammatory mechanism of PPI. In vivo, PPI (1 mg/kg) was administered intragastrically one time a day for 7 weeks starting on the 42nd day after the first immunization with collagen in a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model. Micro-computed Tomography scanning, histological examination, F4/80 and iNOS double immunofluorescent staining and CD4 immunohistochemical staining were performed to determine the effect of PPI treatment on joint structure and inflammation in this model. Results: PPI reduced the inflammatory cytokines production of PEMs stimulated by LPS/IFN-γ, inhibited the phosphorylation of IKKα/β and p65, and prevented p65 nuclear localization. The NF-κB luciferase assay showed that the target of PPI was closely related to the NF-κB pathway. Moreover, NF-κB inhibition, siRNA-mediated knockdown of p65, and p65 overexpression eliminated PPI's inhibitory effect. In addition, PPI attenuated the bone erosion and synovitis, as well as M1-like macrophage and T cell infiltration, in the ankle joint of the CIA model. Conclusion: PPI demonstrated effective amelioration of synovial inflammation in the ankle joint of CIA mice while suppressing NF-κB-mediated production of pro-inflammatory effectors in activated macrophages.
Keywords: NF-κB; collagen-induced arthritis; inflammation; polyphyllin I; primary macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chebulanin exerts its anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects via inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK activation in collagen-induced arthritis mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106823. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106823. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32795901
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
Triphala herbal extract suppresses inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and adjuvant-induced arthritic rats via inhibition of NF-κB pathway.J Immunotoxicol. 2016 Jul;13(4):509-25. doi: 10.3109/1547691X.2015.1136010. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Immunotoxicol. 2016. PMID: 27438966
-
Novel pro-inflammatory interleukins: potential therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis.Joint Bone Spine. 2001 Dec;68(6):477-81. doi: 10.1016/s1297-319x(01)00310-4. Joint Bone Spine. 2001. PMID: 11808983 Review.
-
Anti-cancer effects of Polyphyllin I: An update in 5 years.Chem Biol Interact. 2020 Jan 25;316:108936. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108936. Epub 2019 Dec 20. Chem Biol Interact. 2020. PMID: 31870841 Review.
Cited by
-
Paris polyphylla ethanol extract induces G2/M arrest and suppresses migration and invasion in bladder cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Oct;9(10):5994-6004. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1512. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117211 Free PMC article.
-
Polyphyllin Ⅲ regulates EMT of lung cancer cells through GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jan 15;86(3):1376-1385. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001629. eCollection 2024 Mar. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38463106 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-1224-5p attenuates polycystic ovary syndrome through inhibiting NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation via targeting Forkhead box O 1.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8555-8569. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1987125. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34637688 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3G exacerbates joint inflammation through the accumulation and proliferation of macrophages in the synovium.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Jun 4;24(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02817-7. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35659346 Free PMC article.
-
Global scientific trends update on macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric and visualized analysis from 2000 to 2022.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 9;9(9):e19761. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19761. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

