Screening of herbal extracts for TLR2- and TLR4-dependent anti-inflammatory effects
- PMID: 30307962
- PMCID: PMC6181297
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203907
Screening of herbal extracts for TLR2- and TLR4-dependent anti-inflammatory effects
Abstract
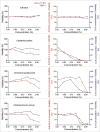
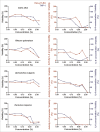
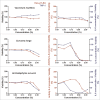
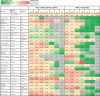
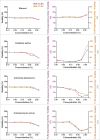
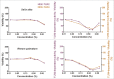
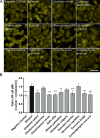
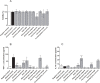
Herbal extracts represent an ample source of natural compounds, with potential to be used in improving human health. There is a growing interest in using natural extracts as possible new treatment strategies for inflammatory diseases. We therefore aimed at identifying herbal extracts that affect inflammatory signaling pathways through toll-like receptors (TLRs), TLR2 and TLR4. Ninety-nine ethanolic extracts were screened in THP-1 monocytes and HeLa-TLR4 transfected reporter cells for their effects on stimulated TLR2 and TLR4 signaling pathways. The 28 identified anti-inflammatory extracts were tested in comparative assays of stimulated HEK-TLR2 and HEK-TLR4 transfected reporter cells to differentiate between direct TLR4 antagonistic effects and interference with downstream signaling cascades. Furthermore, the ten most effective anti-inflammatory extracts were tested on their ability to inhibit nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) translocation in HeLa-TLR4 transfected reporter cell lines and for their ability to repolarize M1-type macrophages. Ethanolic extracts which showed the highest anti-inflammatory potential, up to a complete inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production were Castanea sativa leaves, Cinchona pubescens bark, Cinnamomum verum bark, Salix alba bark, Rheum palmatum root, Alchemilla vulgaris plant, Humulus lupulus cones, Vaccinium myrtillus berries, Curcuma longa root and Arctostaphylos uva-ursi leaves. Moreover, all tested extracts mitigated not only TLR4, but also TLR2 signaling pathways. Seven of them additionally inhibited translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus. Two of the extracts showed impact on repolarization of pro-inflammatory M1-type to anti-inflammatory M2-type macrophages. Several promising anti-inflammatory herbal extracts were identified in this study, including extracts with previously unknown influence on key TLR signaling pathways and macrophage repolarization, serving as a basis for novel lead compound identification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of cinnamon extract and identification of active compounds influencing the TLR2 and TLR4 signaling pathways.Food Funct. 2018 Nov 14;9(11):5950-5964. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01286e. Food Funct. 2018. PMID: 30379176
-
Ocimum sanctum leaf extracts attenuate human monocytic (THP-1) cell activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 28;154(1):148-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.049. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24732112
-
Water extract of Cynanchi atrati Radix regulates inflammation and apoptotic cell death through suppression of IKK-mediated NF-κB signaling.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Sep 1;137(1):626-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.06.022. Epub 2011 Jun 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21718772
-
TLR2 and TLR4 expression during bacterial infections.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(32):4185-93. doi: 10.2174/138161206778743547. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 17100621 Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Extracts and Pure Compounds Derived from Plants via Modulation of Signaling Pathways, Especially PI3K/AKT in Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 16;21(24):9605. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249605. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory potential of aspergillus unguis SP51-EGY: TLR4-dependent effects & chemical diversity via Q-TOF LC-HRMS.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 18;24(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00890-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39294631 Free PMC article.
-
Alchemilla vulgaris modulates isoproterenol-induced cardiotoxicity: interplay of oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and apoptosis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1394557. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394557. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39170697 Free PMC article.
-
The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Wild Bilberry Fruit Extracts Embedded in Mesoporous Silica-Type Supports: A Stability Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;13(2):250. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020250. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397847 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of the benefits of drinking craft beer: Role of phenolic content in health and possible potential of the alcoholic fraction.Curr Res Food Sci. 2023 Mar 4;6:100477. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100477. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 36935850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheum rhaponticum and Rheum rhabarbarum Extracts as Modulators of Endothelial Cell Inflammatory Response.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 14;15(4):949. doi: 10.3390/nu15040949. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839307 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

