Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase exerts a hypoglycemic effect by improving β cell function via inhibition of β cell apoptosis in db/db mice
- PMID: 30284474
- PMCID: PMC6179047
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1477138
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase exerts a hypoglycemic effect by improving β cell function via inhibition of β cell apoptosis in db/db mice
Abstract
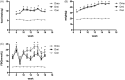
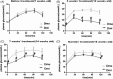
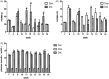
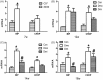
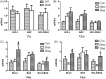
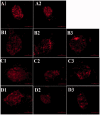
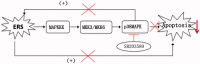
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and inflammation, which may play an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate whether p38 MAPK contributes to the pathogenesis of T2DM. 6-week-old female db/db mice were randomly assigned to Dmo and Dmi groups, and C57 mice were assigned as controls. The Dmi group was gavaged with the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 for 9 weeks, and the effects on β cell dysfunction and apoptosis were investigated. db/db mice showed higher food intake, body mass, fasting glucose, and plasma insulin levels than C57 mice. After SB203580 administration, blood glucose was significantly lower. HOMA β and HOMA IR were improved. Islet mRNA expression levels of the ERS markers were lower. P38 MAPK inhibition reduced blood glucose and improved β cell function, at least in part by reducing β cell apoptosis.
Keywords: SB203580; endoplasmic reticulum stress; p38 MAPK; type 2 diabetes; β cell function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein phosphatase 5 mediate glucocorticoid-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic islets and β-cells.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Mar 5;383(1-2):126-36. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.010. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24361515
-
In type 2 diabetes induced by cigarette smoking, activation of p38 MAPK is involved in pancreatic β-cell apoptosis.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Apr;25(10):9817-9827. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1337-3. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29372523
-
Protective effects of SGLT2 inhibitor luseogliflozin on pancreatic β-cells in obese type 2 diabetic db/db mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Feb 12;470(3):772-782. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.109. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 26505796
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: a critical node linking insulin resistance and cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Mar;9(1):38-46. doi: 10.2174/187153009787582397. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19275680 Review.
-
Roles of p38-MAPK in insulin resistant heart: evidence from bench to future bedside application.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(32):5742-54. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319320009. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448488 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Apoptosis Induction and Its Regulation by Fatty Acids in Pancreatic β-Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4285. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084285. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin Promotes the Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Regulating TGF-β Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 15;9:722365. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.722365. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34722505 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Conventional and Atypical MAPKs on the Development of Metabolic Diseases.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 29;10(9):1256. doi: 10.3390/biom10091256. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32872540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting β-cell dedifferentiation and transdifferentiation: opportunities and challenges.Endocr Connect. 2021 Aug 13;10(8):R213-R228. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0260. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 34289444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment improves pancreatic β‑cell function and hepatic gluconeogenesis in STZ‑induced type‑2 diabetes mellitus model mice.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Mar;25(3):90. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12606. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35039874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhodes CJ.Type 2 diabetes-a matter of beta-cell life and death? Science 2005;307:380–4. - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE.Clinical review 135: The importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4047–58. - PubMed
-
- Donath MY, Ehses JA, Maedler K, et al. . Mechanisms of beta-cell death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2005;54 (Suppl 2):S108–S13. - PubMed
-
- Lomas DA, Lipson DA, Miller BE, et al. . An oral inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase reduces plasma fibrinogen in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Pharmacol 2012;52:416–24. - PubMed
-
- Elkhawad M, Rudd JH, Sarov-Blat L, et al. . Effects of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition on vascular and systemic inflammation in patients with atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imag 2012;5:911–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
