Do liposomal bupivacaine infiltration and interscalene nerve block provide similar pain relief after total shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30271195
- PMCID: PMC6151095
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S177716
Do liposomal bupivacaine infiltration and interscalene nerve block provide similar pain relief after total shoulder arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Controversy still exists regarding the efficiency and safety of liposomal bupivacaine (LB) vs interscalene nerve block (INB) for pain management after total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA). The aim of the present meta-analysis was to perform a relatively credible and overall assessment to compare the efficiency and safety of LB-based infiltration vs INB for pain management after TSA.
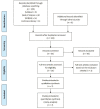
Methods: The PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and EMBASE were systematically searched. Only studies published up to March 2018 comparing LB vs INB for pain control after TSA were included. The primary outcome extracted from the studies was postoperative pain score at different periods. The secondary outcomes included total opioid consumption, length of hospital stay, and complications.
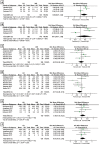
Results: Seven studies with 707 patients were included in this study. No statistically significant difference was observed between the LB and INB groups in pain scores at 8 hours, 12 hours, 24 hours, postoperative day (POD) 1, and POD 2. The two groups also showed comparable total opioid consumption at POD 0, POD 1, POD 2, and length of hospital stay. The LB group had a significantly higher pain score at 4 hours (standard mean difference =0.65, 95% CI=0.07 to 1.24, P=0.03) but a lower occurrence rate of complications than did the INB group (OR =0.51, 95% CI=0.28 to 0.91, P=0.02).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis revealed that INB provides excellent analgesic effects within 4 hours after TSA, while patients treated with LB infiltration experienced significantly less occurrence rate of complications after TSA. In general, both approaches provide similar overall pain relief and have similar opioid consumption after TSA, with no significant difference in the length of hospital stay. Nevertheless, more high-quality randomized controlled trails with long-term follow-up are still required to make the final conclusion.
Keywords: interscalene nerve block; liposomal bupivacaine; meta-analysis; total shoulder arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Liposomal bupivacaine versus interscalene nerve block for pain control after shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective randomized trial.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016 Nov;25(11):1742-1748. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.007. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016. PMID: 27422692 Clinical Trial.
-
Liposomal bupivacaine versus interscalene nerve block for pain control after shoulder arthroplasty: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jul;96(27):e7226. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007226. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28682872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periarticular injection in addition to interscalene nerve block can decrease opioid consumption and pain following total shoulder arthroplasty: a comparison cohort study.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023 Dec;32(12):e597-e607. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.05.009. Epub 2023 Jun 11. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023. PMID: 37311486
-
Comparison of liposomal bupivacaine infiltration versus interscalene nerve block for pain control in total shoulder arthroplasty: A meta-analysis of randomized control trails.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(39):e8079. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008079. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28953626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liposomal bupivacaine provides superior pain control compared to bupivacaine with adjuvants in interscalene block for total shoulder replacement: a prospective double-blinded, randomized controlled trial.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 Jul;33(7):1512-1520. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.12.014. Epub 2024 Feb 3. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 38311100 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Osmotically balanced, large unilamellar liposomes that enable sustained bupivacaine release for prolonged pain relief in in vivo rat models.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 8;11(1):12096. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91624-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34103656 Free PMC article.
-
Practical Regional Anesthesia Guide for Elderly Patients.Drugs Aging. 2019 Mar;36(3):213-234. doi: 10.1007/s40266-018-00631-y. Drugs Aging. 2019. PMID: 30680678 Review.
-
Patient Complications after Interscalene Block: A Retrospective Comparison of Liposomal Bupivacaine to Nonliposomal Bupivacaine.Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2020 Mar 27;2020:6704303. doi: 10.1155/2020/6704303. eCollection 2020. Anesthesiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32280340 Free PMC article.
-
[Liposomal bupivacaine-No breakthrough in postoperative pain management].Anaesthesiologie. 2022 Jul;71(7):556-564. doi: 10.1007/s00101-022-01118-7. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Anaesthesiologie. 2022. PMID: 35469071 Review. German.
-
The use of liposomal bupivacaine in fracture surgery: a review.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Apr 1;18(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03583-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37005638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bryant D, Litchfield R, Sandow M, Gartsman GM, Guyatt G, Kirkley A. A comparison of pain, strength, range of motion, and functional outcomes after hemiarthroplasty and total shoulder arthroplasty in patients with osteoarthritis of the shoulder. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(9):1947–1956. - PubMed
-
- Deshmukh AV, Koris M, Zurakowski D, Thornhill TS. Total shoulder arthroplasty: long-term survivorship, functional outcome, and quality of life. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(5):471–479. - PubMed
-
- Kim SH, Wise BL, Zhang Y, Szabo RM. Increasing incidence of shoulder arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(24):2249–2254. - PubMed
-
- Mahoney A, Bosco JA, 3rd, Zuckerman JD. Readmission after shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(3):377–381. - PubMed
-
- Schairer WW, Zhang AL, Feeley BT. Hospital readmissions after primary shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(9):1349–1355. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

