xCT inhibition sensitizes tumors to γ-radiation via glutathione reduction
- PMID: 30190786
- PMCID: PMC6122354
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25794
xCT inhibition sensitizes tumors to γ-radiation via glutathione reduction
Abstract
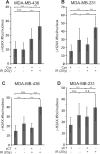
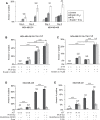
About 3 million US cancer patients and 1.7 million EU cancer patients received multiple doses of radiation therapy (RT) in 2012, with treatment duration limited by normal adjacent tissue damage. Tumor-specific sensitization could allow treatment with lower radiation doses, reducing normal tissue damage. This is a longstanding, largely unrealized therapeutic goal. The cystine:glutamate exchanger xCT is expressed on poor prognosis subsets of most solid tumors, but not on most normal cells. xCT provides cells with environmental cystine for enhanced glutathione synthesis. Glutathione is used to control reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are therapeutic effectors of RT. We tested whether xCT inhibition would sensitize xCT+ tumor cells to ionizing radiation. We found that pretreatment with the xCT inhibitor erastin potently sensitized xCT+ but not xCT- cells, in vitro and in xenograft. Similarly, targeted gene inactivation also sensitized cells, and both modes of sensitization were overcome by glutathione supplementation. Sensitization prolongs DNA damage signaling, increases genome instability, and enhances cell death, revealing an unforeseen role for cysteine in genome integrity maintenance. We conclude that an xCT-specific therapeutic would provide tumor-specific sensitization to RT, allowing treatment with lower radiation doses, and producing far fewer side effects than other proposed sensitizers. Our data speaks to the need for the rapid development of such a drug.
Keywords: SLC7A11; glutathione; radiation sensitize; radiation therapy; xCT.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
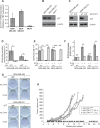
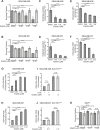
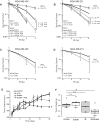
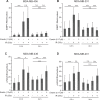

Similar articles
-
Genetic Ablation of the Cystine Transporter xCT in PDAC Cells Inhibits mTORC1, Growth, Survival, and Tumor Formation via Nutrient and Oxidative Stresses.Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 1;79(15):3877-3890. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-3855. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31175120
-
Temozolomide toxicity operates in a xCT/SLC7a11 dependent manner and is fostered by ferroptosis.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):74630-74647. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11858. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27612422 Free PMC article.
-
Erastin sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by restraining xCT and cystathionine-γ-lyase function.Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1465-74. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3712. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25585997
-
Regulation of xCT expression and system x (c) (-) function in neuronal cells.Amino Acids. 2012 Jan;42(1):171-9. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-0862-x. Epub 2011 Mar 3. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 21369940 Review.
-
Emerging Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials for Cancer Radiation Therapy.Adv Mater. 2017 Aug;29(32). doi: 10.1002/adma.201700996. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Adv Mater. 2017. PMID: 28643452 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction and application of ferroptosis in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Jan 7;22(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02366-0. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 34996454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current understanding of ferroptosis in the progression and treatment of pancreatic cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Sep 9;21(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02166-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34503532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nature-Inspired Bioactive Compounds: A Promising Approach for Ferroptosis-Linked Human Diseases?Molecules. 2023 Mar 14;28(6):2636. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062636. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glioblastomas: Hijacking Metabolism to Build a Flexible Shield for Therapy Resistance.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Nov;39(13-15):957-979. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0088. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 37022791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Rewiring in Radiation Oncology Toward Improving the Therapeutic Ratio.Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:653621. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.653621. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041023 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berkey FJ. Managing the adverse effects of radiation therapy. Am Fam Physician. 2010;82:381–8. 394. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

