Transcription Elongation Can Affect Genome 3D Structure
- PMID: 30146161
- PMCID: PMC6130916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.047
Transcription Elongation Can Affect Genome 3D Structure
Abstract
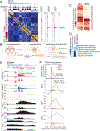
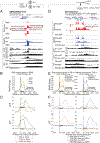
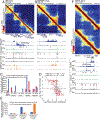
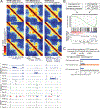
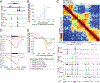
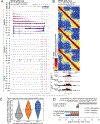
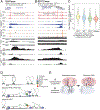
How transcription affects genome 3D organization is not well understood. We found that during influenza A (IAV) infection, rampant transcription rapidly reorganizes host cell chromatin interactions. These changes occur at the ends of highly transcribed genes, where global inhibition of transcription termination by IAV NS1 protein causes readthrough transcription for hundreds of kilobases. In these readthrough regions, elongating RNA polymerase II disrupts chromatin interactions by inducing cohesin displacement from CTCF sites, leading to locus decompaction. Readthrough transcription into heterochromatin regions switches them from the inert (B) to the permissive (A) chromatin compartment and enables transcription factor binding. Data from non-viral transcription stimuli show that transcription similarly affects cohesin-mediated chromatin contacts within gene bodies. Conversely, inhibition of transcription elongation allows cohesin to accumulate at previously transcribed intragenic CTCF sites and to mediate chromatin looping and compaction. Our data indicate that transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II remodels genome 3D architecture.
Keywords: CTCF; NS1; chromatin compaction; cohesin; genome 3D structure; influenza A virus; readthrough transcription; transcription; transcription elongation; transcription termination.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structural basis for cohesin-CTCF-anchored loops.Nature. 2020 Feb;578(7795):472-476. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1910-z. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Nature. 2020. PMID: 31905366 Free PMC article.
-
Topologically associating domains and chromatin loops depend on cohesin and are regulated by CTCF, WAPL, and PDS5 proteins.EMBO J. 2017 Dec 15;36(24):3573-3599. doi: 10.15252/embj.201798004. Epub 2017 Dec 7. EMBO J. 2017. PMID: 29217591 Free PMC article.
-
ESCO1 and CTCF enable formation of long chromatin loops by protecting cohesinSTAG1 from WAPL.Elife. 2020 Feb 17;9:e52091. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52091. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32065581 Free PMC article.
-
CTCF as a boundary factor for cohesin-mediated loop extrusion: evidence for a multi-step mechanism.Nucleus. 2020 Dec;11(1):132-148. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2020.1782024. Nucleus. 2020. PMID: 32631111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A tour of 3D genome with a focus on CTCF.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Jun;90:4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.07.020. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30031214 Review.
Cited by
-
H3K27ac bookmarking promotes rapid post-mitotic activation of the pluripotent stem cell program without impacting 3D chromatin reorganization.Mol Cell. 2021 Apr 15;81(8):1732-1748.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.02.032. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33730542 Free PMC article.
-
Long Noncoding RNAs-Crucial Players Organizing the Landscape of the Neuronal Nucleus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;22(7):3478. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073478. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRF8 Is an AML-Specific Susceptibility Factor That Regulates Signaling Pathways and Proliferation of AML Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;13(4):764. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040764. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673123 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Changes in Histone Modifications Are Associated with Differential Chromatin Interactions.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 26;15(8):988. doi: 10.3390/genes15080988. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202349 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct negative-sense RNA viruses induce a common set of transcripts encoding proteins forming an extensive network.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0093524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00935-24. Epub 2024 Sep 16. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39283124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey JA, Gu Z, Clark RA, Reinert K, Samonte RV, Schwartz S, Adams MD, Myers EW, Li PW, and Eichler EE (2002). Recent segmental duplications in the human genome. Science 297, 1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

