Mechanism of calmodulin inactivation of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6
- PMID: 30116787
- PMCID: PMC6093632
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau6088
Mechanism of calmodulin inactivation of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6
Abstract
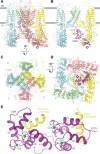
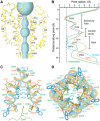
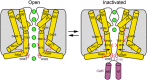
Calcium (Ca2+) plays a major role in numerous physiological processes. Ca2+ homeostasis is tightly controlled by ion channels, the aberrant regulation of which results in various diseases including cancers. Calmodulin (CaM)-mediated Ca2+-induced inactivation is an ion channel regulatory mechanism that protects cells against the toxic effects of Ca2+ overload. We used cryo-electron microscopy to capture the epithelial calcium channel TRPV6 (transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 6) inactivated by CaM. The TRPV6-CaM complex exhibits 1:1 stoichiometry; one TRPV6 tetramer binds both CaM lobes, which adopt a distinct head-to-tail arrangement. The CaM carboxyl-terminal lobe plugs the channel through a unique cation-π interaction by inserting the side chain of lysine K115 into a tetra-tryptophan cage at the pore's intracellular entrance. We propose a mechanism of CaM-mediated Ca2+-induced inactivation that can be explored for therapeutic design.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure and function of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6.J Physiol. 2021 May;599(10):2673-2697. doi: 10.1113/JP279024. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32073143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Mechanism for Calmodulin-Dependent Inactivation of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 6.Biochemistry. 2018 May 8;57(18):2611-2622. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01286. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29505720
-
Regulation of the mouse epithelial Ca2(+) channel TRPV6 by the Ca(2+)-sensor calmodulin.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 9;279(28):28855-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313637200. Epub 2004 Apr 30. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15123711
-
Opening of the human epithelial calcium channel TRPV6.Nature. 2018 Jan 11;553(7687):233-237. doi: 10.1038/nature25182. Epub 2017 Dec 20. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29258289 Free PMC article.
-
What structures did, and did not, reveal about the function of the epithelial Ca2+ channels TRPV5 and TRPV6.Cell Calcium. 2022 Sep;106:102620. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2022.102620. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Cell Calcium. 2022. PMID: 35834842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular Helix-Loop-Helix Domain Modulates Inactivation Kinetics of Mammalian TRPV5 and TRPV6 Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4470. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054470. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901904 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium selective channel TRPV6: Structure, function, and implications in health and disease.Gene. 2022 Apr 5;817:146192. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146192. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Gene. 2022. PMID: 35031425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 5;8(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37402746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global alignment and assessment of TRP channel transmembrane domain structures to explore functional mechanisms.Elife. 2020 Aug 17;9:e58660. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58660. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32804077 Free PMC article.
-
CaV channels reject signaling from a second CaM in eliciting Ca2+-dependent feedback regulation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 30;295(44):14948-14962. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013777. Epub 2020 Aug 20. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32820053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marchi S., Pinton P., Alterations of calcium homeostasis in cancer cells. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 29, 1–6 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Lee A., Wong S. T., Gallagher D., Li B., Storm D. R., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A., Ca2+/calmodulin binds to and modulates P/Q-type calcium channels. Nature 399, 155–159 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

