riboWaltz: Optimization of ribosome P-site positioning in ribosome profiling data
- PMID: 30102689
- PMCID: PMC6112680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006169
riboWaltz: Optimization of ribosome P-site positioning in ribosome profiling data
Abstract
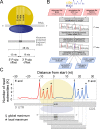
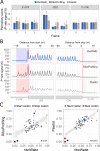
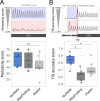
Ribosome profiling is a powerful technique used to study translation at the genome-wide level, generating unique information concerning ribosome positions along RNAs. Optimal localization of ribosomes requires the proper identification of the ribosome P-site in each ribosome protected fragment, a crucial step to determine the trinucleotide periodicity of translating ribosomes, and draw correct conclusions concerning where ribosomes are located. To determine the P-site within ribosome footprints at nucleotide resolution, the precise estimation of its offset with respect to the protected fragment is necessary. Here we present riboWaltz, an R package for calculation of optimal P-site offsets, diagnostic analysis and visual inspection of ribosome profiling data. Compared to existing tools, riboWaltz shows improved accuracies for P-site estimation and neat ribosome positioning in multiple case studies. riboWaltz was implemented in R and is available as an R package at https://github.com/LabTranslationalArchitectomics/RiboWaltz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Active Ribosome Profiling with RiboLace: From Bench to Data Analysis.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2252:201-220. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1150-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33765277
-
The extent of ribosome queuing in budding yeast.PLoS Comput Biol. 2018 Jan 29;14(1):e1005951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005951. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018. PMID: 29377894 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Ribosome Positioning on Translating Transcripts with Ribosome Profiling.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1358:71-97. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3067-8_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26463378
-
Ribosome profiling: a Hi-Def monitor for protein synthesis at the genome-wide scale.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Sep-Oct;4(5):473-90. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1172. Epub 2013 May 20. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23696005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Ribosome profiling as an innovative tool to study the process of protein synthesis].Postepy Biochem. 2019 Mar 22;65(1):41-51. doi: 10.18388/pb.2019_255. Postepy Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30901182 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
New Insights into Phase Separation Processes and Membraneless Condensates of EIN2.Plants (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;11(16):2149. doi: 10.3390/plants11162149. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015451 Free PMC article.
-
Seryl-tRNA synthetase promotes translational readthrough by mRNA binding and involvement of the selenocysteine incorporation machinery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Oct 27;51(19):10768-10781. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad773. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37739431 Free PMC article.
-
A Unified Model for the Function of YTHDF Proteins in Regulating m6A-Modified mRNA.Cell. 2020 Jun 25;181(7):1582-1595.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32492408 Free PMC article.
-
An mRNA processing pathway suppresses metastasis by governing translational control from the nucleus.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;25(6):892-903. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01141-9. Epub 2023 May 8. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37156909 Free PMC article.
-
Pleiotropic effects of PAB1 deletion: Extensive changes in the yeast proteome, transcriptome, and translatome.PLoS Genet. 2024 Sep 5;20(9):e1011392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011392. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 39236083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steitz JA. Polypeptide chain initiation: nucleotide sequences of the three ribosomal binding sites in bacteriophage R17 RNA. Nature. 1969;224: 957–64. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/5360547 - PubMed
-
- Wolin SL, Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988;7: 3559–69. Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=454858&tool=pm... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

