Early antiretroviral therapy limits SIV reservoir establishment to delay or prevent post-treatment viral rebound
- PMID: 30082858
- PMCID: PMC6389357
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0130-7
Early antiretroviral therapy limits SIV reservoir establishment to delay or prevent post-treatment viral rebound
Abstract
Prophylactic vaccination of rhesus macaques with rhesus cytomegalovirus (RhCMV) vectors expressing simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) antigens (RhCMV/SIV) elicits immune responses that stringently control highly pathogenic SIV infection, with subsequent apparent clearance of the infection, in ~50% of vaccinees. In contrast, here, we show that therapeutic RhCMV/SIV vaccination of rhesus macaques previously infected with SIV and given continuous combination antiretroviral therapy (cART) beginning 4-9 d post-SIV infection does not mediate measurable SIV reservoir clearance during over 600 d of follow-up on cART relative to RhCMV/control vaccination. However, none of the six animals started on cART on day four or five, across both RhCMV/SIV- and RhCMV/control-vaccinated groups, those rhesus macaques with SIV reservoirs most closely resembling those of prophylactically RhCMV/SIV-vaccinated and protected animals early in their course, showed post-cART viral rebound with up to nine months of follow-up. Moreover, at necropsy, these rhesus macaques showed little to no evidence of replication-competent SIV. These results suggest that the early SIV reservoir is limited in durability and that effective blockade of viral replication and spread in this critical time window by either pharmacologic or immunologic suppression may result in reduction, and potentially loss, of rebound-competent virus over a period of ~two years.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


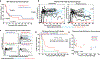
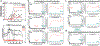
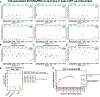
Similar articles
-
Evaluating the Intactness of Persistent Viral Genomes in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques after Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy within One Year of Infection.J Virol. 2019 Dec 12;94(1):e01308-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01308-19. Print 2019 Dec 12. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31597776 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbated AIDS Progression by PD-1 Blockade during Therapeutic Vaccination in Chronically Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques after Interruption of Antiretroviral Therapy.J Virol. 2022 Feb 9;96(3):e0178521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01785-21. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34818070 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Proviral DNA in Circulating Cells Correlates with Plasma Viral Rebound in Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques after Antiretroviral Therapy Interruption.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02064-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02064-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33408173 Free PMC article.
-
Brain macrophages harbor latent, infectious simian immunodeficiency virus.AIDS. 2019 Dec 1;33 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S181-S188. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002269. AIDS. 2019. PMID: 31789817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations in the development of nonhuman primate models of combination antiretroviral therapy for studies of AIDS virus suppression, residual virus, and curative strategies.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013 Jul;8(4):262-72. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e328361cf40. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2013. PMID: 23698559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity of the Replication-Competent HIV Reservoir in Treated Patients.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0078422. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00784-22. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35770985 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of initiation of anti-retroviral therapy predicts post-treatment control of SIV replication.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Oct 6;19(10):e1011660. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011660. eCollection 2023 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37801446 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-15 response signature predicts RhCMV/SIV vaccine efficacy.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jul 6;17(7):e1009278. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009278. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34228762 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating a New Class of AKT/mTOR Activators for HIV Latency Reversing Activity Ex Vivo and In Vivo.J Virol. 2021 Mar 25;95(8):e02393-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02393-20. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33536176 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal integrin α4β7 blockade fails to reduce the seeding and size of viral reservoirs in SIV-infected rhesus macaques.FASEB J. 2021 Feb;35(2):e21282. doi: 10.1096/fj.202002235R. FASEB J. 2021. PMID: 33484474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Churchill MJ, et al. HIV reservoirs: what, where and how to target them. Nat Rev Microbiol 14, 55–60 (2016). - PubMed
METHODS REFERENCES
-
- Cline AN, et al. Highly sensitive SIV plasma viral load assay: practical considerations, realistic performance expectations, and application to reverse engineering of vaccines for AIDS. J Med Primatol 34, 303–312 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Venneti S, et al. Longitudinal in vivo positron emission tomography imaging of infected and activated brain macrophages in a macaque model of human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis correlates with central and peripheral markers of encephalitis and areas of synaptic degeneration. Am J Pathol 172, 1603–1616 (2008). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

