Sphingosine Kinase Regulates Neuropeptide Secretion During the Oxidative Stress-Response Through Intertissue Signaling
- PMID: 30082417
- PMCID: PMC6146497
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0536-18.2018
Sphingosine Kinase Regulates Neuropeptide Secretion During the Oxidative Stress-Response Through Intertissue Signaling
Abstract
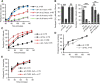
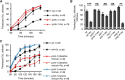
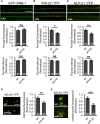
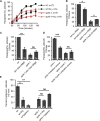
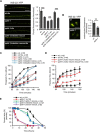
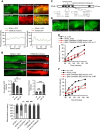
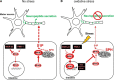
The Nrf2 antioxidant transcription factor promotes redox homeostasis in part through reciprocal signaling between neurons and neighboring cells, but the signals involved in intertissue signaling in response to Nrf2 activation are not well defined. In Caenorhabditis elegans, activation of SKN-1/Nrf2 in the intestine negatively regulates neuropeptide secretion from motor neurons. Here, we show that sphingosine kinase (SPHK-1) functions downstream of SKN-1/Nrf2 in the intestine to regulate neuropeptide secretion from motor neurons during the oxidative stress response in C. elegans hermaphrodites. SPHK-1 localizes to mitochondria in the intestine and SPHK-1 mitochondrial localization and kinase activity are essential for its function in regulating motor neuron function. SPHK-1 is recruited to mitochondria from cytosolic pools and its mitochondrial abundance is negatively regulated by acute or chronic SKN-1 activation. Finally, the regulation of motor function by SKN-1 requires the activation of the p38 MAPK cascade in the intestine and occurs through controlling the biogenesis or maturation of dense core vesicles in motor neurons. These findings show that the inhibition of SPHK-1 in the intestine by SKN-1 negatively regulates neuropeptide secretion from motor neurons, revealing a new mechanism by which SPHK-1 signaling mediates its effects on neuronal function in response to oxidative stress.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Neurons are highly susceptible to damage by oxidative stress, yet have limited capacity to activate the SKN-1/Nrf2 oxidative stress response, relying instead on astrocytes to provide redox homeostasis. In Caenorhabditis elegans, intertissue signaling from the intestine plays a key role in regulating neuronal function during the oxidative stress response. Here, through a combination of genetic, behavioral, and fluorescent imaging approaches, we found that sphingosine kinase functions in the SKN-1/Nrf2 pathway in the intestine to regulate neuropeptide biogenesis and secretion in motor neurons. These results implicate sphingolipid signaling as a new component of the oxidative stress response and suggest that C. elegans may be a genetically tractable model to study non-cell-autonomous oxidative stress signaling to neurons.
Keywords: Nrf2/SKN-1; mitochondria; motor neuron; neuropeptide; oxidative stress; sphingosine kinase.
Copyright © 2018 the authors 0270-6474/18/388160-17$15.00/0.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Network Regulates Neuromuscular Function in Response to Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2019 Apr;211(4):1283-1295. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302026. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30782598 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine Kinase Activates the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Is Targeted to Mitochondria by Stress.Cell Rep. 2018 Sep 11;24(11):2932-2945.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.037. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30208318 Free PMC article.
-
TRX-1 Regulates SKN-1 Nuclear Localization Cell Non-autonomously in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):387-402. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.185272. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26920757 Free PMC article.
-
SKN-1/Nrf, stress responses, and aging in Caenorhabditis elegans.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):290-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26232625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian control of BDNF-mediated Nrf2 activation in astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from ferroptosis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Mar;133:169-178. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.09.002. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30189266 Review.
Cited by
-
A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Network Regulates Neuromuscular Function in Response to Oxidative Stress in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2019 Apr;211(4):1283-1295. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302026. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 30782598 Free PMC article.
-
In the Model Host Caenorhabditis elegans, Sphingosine-1-Phosphate-Mediated Signaling Increases Immunity toward Human Opportunistic Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 22;21(21):7813. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217813. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33105563 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress in Wernicke's encephalopathy.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 May 16;15:1150878. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1150878. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37261263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide kinase-mediated C1P metabolism attenuates acute liver injury by inhibiting the interaction between KEAP1 and NRF2.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Apr;56(4):946-958. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01203-4. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38556546 Free PMC article.
-
FSHR-1/GPCR Regulates the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2020 Feb;214(2):409-418. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302947. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Genetics. 2020. PMID: 31801834 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
