Formononetin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetic Rats Reduces Insulin Resistance and Hyperglycemia
- PMID: 30072892
- PMCID: PMC6058024
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00739
Formononetin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetic Rats Reduces Insulin Resistance and Hyperglycemia
Abstract
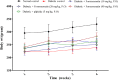
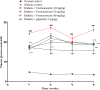
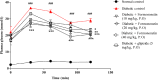
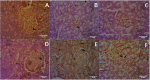
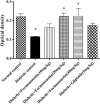
Type 2 diabetic mellitus is a multifactorial metabolic disorder affecting huge population around the world. This indicates that there is an urgent unmet need of cost effective, new treatment strategies for type 2 diabetes mellitus with no or less side effects. Phenolic compounds including isoflavones are known for their beneficial effect in metabolic disorders. The present work was intended to find out efficacy of formononetin, an isoflavone treatment in experimental model of type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes mellitus was induced by feeding high fat diet for 2 weeks prior to streptozotocin administration in Sprague Dawley rats. Diabetic animals were treated with formononetin for 28 days at three dose level, i.e., 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg body weight orally. The effect of formononetin treatment on various parameters such as plasma glucose, glucose tolerance, insulin, HOMA-IR, lipid profile, hepatic glycogen content, glycohaemoglobin and SIRT1 expression in pancreatic tissue was measured. Histopathological changes in pancreatic tissue were also studied. Results of the study demonstrate that formononetin treatment reduces blood glucose level significantly (p < 0.001) at all the three dose level. It also improved glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and lipid profile along with reduction in glycohaemoglobin content in blood. Formononetin treatment also improved hepatic glycogen level profoundly in diabetic rats. Determination of SIRT1 expression in pancreatic tissue by immunohistochemical analysis showed that formononetin treatment increases the expression of SIRT1 in pancreatic tissue. Histopathological study showed that treatment with formononetin protects pancreatic beta cells from necro-degeneration and atrophic effect. It can be concluded that formononetin treatment reduces insulin resistance and attenuate hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes which may be due to increasing expression of SIRT1 in pancreatic tissues.
Keywords: SIRT1; formononetin; high fat diet; isoflavone; streptozotocin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biochanin A improves insulin sensitivity and controls hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:1119-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.073. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30257324
-
Trifolium pratense (Red Clover) Improve SIRT1 Expression and Glycogen Content in High Fat Diet-Streptozotocin Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Rats.Chem Biodivers. 2020 Apr;17(4):e2000019. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202000019. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Chem Biodivers. 2020. PMID: 32187456
-
Formononetin attenuates kidney damage in type 2 diabetic rats.Life Sci. 2019 Feb 15;219:109-121. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.013. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30641085
-
Formononetin Ameliorates Diabetic Neuropathy by Increasing Expression of SIRT1 and NGF.Chem Biodivers. 2020 Jun;17(6):e2000162. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202000162. Epub 2020 May 27. Chem Biodivers. 2020. PMID: 32459048
-
Cellular Senescence in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct Senotherapeutic Strategies for Adipose Tissue and Pancreatic β Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 31;13:869414. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.869414. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35432205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotherapy targeting the obese white adipose tissue microenvironment: Focus on non-communicable diseases.Bioact Mater. 2024 Feb 19;35:461-476. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.01.027. eCollection 2024 May. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38404641 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targets and mechanisms of Jiawei Jiaotai Pill on diabetic cardiomyopathy based on network pharmacology.World J Diabetes. 2023 Nov 15;14(11):1659-1671. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i11.1659. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 38077804 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Phytoestrogens and Their Metabolites as Epigenetic Modulators with Impact on Human Health.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;10(12):1893. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121893. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the botany, phytochemistry, traditional uses, pharmacology, toxicology, and quality control of the Astragalus memeranaceus.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 23;14:1242318. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1242318. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37680711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hu-Zhang-Qing-Mai-Yin Inhibits Proliferation of Human Retinal Capillary Endothelial Cells Exposed to High Glucose.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 6;12:732655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.732655. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34421625 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

