GABA Levels in Left and Right Sensorimotor Cortex Correlate across Individuals
- PMID: 30042306
- PMCID: PMC6164430
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines6030080
GABA Levels in Left and Right Sensorimotor Cortex Correlate across Individuals
Abstract
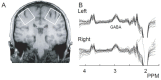
Differences in γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels measured with Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy have been shown to correlate with behavioral performance over a number of tasks and cortical regions. These correlations appear to be regionally and functionally specific. In this study, we test the hypothesis that GABA levels will be correlated within individuals for functionally related regions-the left and right sensorimotor cortex. In addition, we investigate whether this is driven by bulk tissue composition. GABA measurements using edited MRS data were acquired from the left and right sensorimotor cortex in 24 participants. T1-weighted MR images were also acquired and segmented to determine the tissue composition of the voxel. GABA level is shown to correlate significantly between the left and right regions (r = 0.64, p < 0.03). Tissue composition is highly correlated between sides, but does not explain significant variance in the bilateral correlation. In conclusion, individual differences in GABA level, which have previously been described as functionally and regionally specific, are correlated between homologous sensorimotor regions. This correlation is not driven by bulk differences in voxel tissue composition.
Keywords: GABA; MRS; bilateral inhibition; individual differences; sensorimotor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GABA levels and measures of intracortical and interhemispheric excitability in healthy young and older adults: an MRS-TMS study.Neurobiol Aging. 2018 May;65:168-177. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.01.023. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Neurobiol Aging. 2018. PMID: 29494863
-
Macromolecule-suppressed GABA measurements correlate more strongly with behavior than macromolecule-contaminated GABA+ measurements.Brain Res. 2018 Dec 15;1701:204-211. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.021. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30244020 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related differences in GABA levels are driven by bulk tissue changes.Hum Brain Mapp. 2018 Sep;39(9):3652-3662. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24201. Epub 2018 May 2. Hum Brain Mapp. 2018. PMID: 29722142 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression.Magn Reson Med. 2015 Dec;74(6):1523-9. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25549. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Magn Reson Med. 2015. PMID: 25521836 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue correction for GABA-edited MRS: Considerations of voxel composition, tissue segmentation, and tissue relaxations.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Nov;42(5):1431-40. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24903. Epub 2015 Jul 14. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26172043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical GABA Levels Are Reduced in Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome.Brain Sci. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):1666. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13121666. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38137114 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive guide to MEGA-PRESS for GABA measurement.Anal Biochem. 2023 May 15;669:115113. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2023.115113. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Anal Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36958511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased GABA+ in People With Migraine, Headache, and Pain Conditions- A Potential Marker of Pain.J Pain. 2021 Dec;22(12):1631-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jun 25. J Pain. 2021. PMID: 34182103 Free PMC article.
-
GABA and glutamate in the preterm neonatal brain: In-vivo measurement by magnetic resonance spectroscopy.Neuroimage. 2021 Sep;238:118215. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118215. Epub 2021 May 28. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34058332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unaltered Brain GABA Concentrations and Resting fMRI Activity in Functional Dyspepsia With and Without Comorbid Depression.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Sep 11;11:549749. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.549749. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33061916 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

