Mechanotransduction in talin through the interaction of the R8 domain with DLC1
- PMID: 30028837
- PMCID: PMC6054372
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005599
Mechanotransduction in talin through the interaction of the R8 domain with DLC1
Abstract
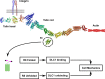
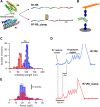
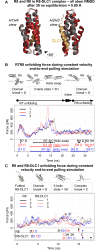
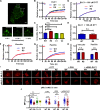
The mechanical unfolding of proteins is a cellular mechanism for force transduction with potentially broad implications in cell fate. Despite this, the mechanism by which protein unfolding elicits differential downstream signalling pathways remains poorly understood. Here, we used protein engineering, atomic force microscopy, and biophysical tools to delineate how protein unfolding controls cell mechanics. Deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1) is a negative regulator of Ras homolog family member A (RhoA) and cell contractility that regulates cell behaviour when localised to focal adhesions bound to folded talin. Using a talin mutant resistant to force-induced unfolding of R8 domain, we show that talin unfolding determines DLC1 downstream signalling and, consequently, cell mechanics. We propose that this new mechanism of mechanotransduction may have implications for a wide variety of associated cellular processes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Full activity of the deleted in liver cancer 1 (DLC1) tumor suppressor depends on an LD-like motif that binds talin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK).Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Oct 11;108(41):17129-34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112122108. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21969587 Free PMC article.
-
LD Motif Recognition by Talin: Structure of the Talin-DLC1 Complex.Structure. 2016 Jul 6;24(7):1130-41. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.04.016. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Structure. 2016. PMID: 27265849 Free PMC article.
-
Talin-mediated force transmission and talin rod domain unfolding independently regulate adhesion signaling.J Cell Sci. 2019 Apr 3;132(7):jcs226514. doi: 10.1242/jcs.226514. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 30837291
-
Talin‑1 interaction network in cellular mechanotransduction (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 May;49(5):60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5116. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35266014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Talin: a mechanosensitive molecule in health and disease.FASEB J. 2016 Jun;30(6):2073-85. doi: 10.1096/fj.201500080R. Epub 2016 Feb 22. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27252130 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanotransduction: from the cell surface to the nucleus via RhoA.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019 Aug 19;374(1779):20180229. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2018.0229. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31431179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial YAP/TAZ Signaling in Angiogenesis and Tumor Vasculature.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 4;10:612802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.612802. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33614496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An efficient alpha helix model and simulation framework for stationary electrostatic interaction force estimation.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88369-3. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907198 Free PMC article.
-
Talin in mechanotransduction and mechanomemory at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2021 Oct 15;134(20):jcs258749. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258749. Epub 2021 Oct 28. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34708856 Free PMC article.
-
ConFERMing the role of talin in integrin activation and mechanosignaling.J Cell Sci. 2023 Apr 15;136(8):jcs260576. doi: 10.1242/jcs.260576. Epub 2023 Apr 20. J Cell Sci. 2023. PMID: 37078342 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

