RIG-I Detects Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Transcripts in a RNA Polymerase III-Independent Manner
- PMID: 29970461
- PMCID: PMC6030556
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00823-18
RIG-I Detects Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Transcripts in a RNA Polymerase III-Independent Manner
Abstract
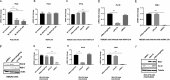
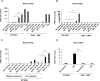
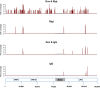
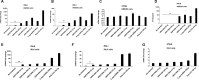
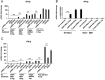
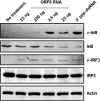
Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) is a cytosolic pathogen recognition receptor that initiates the innate immune response against many RNA viruses. We previously showed that RIG-I restricts Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) reactivation (J. A. West et al., J Virol 88:5778-5787, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03226-13). In this study, we report that KSHV stimulates the RIG-I signaling pathway in a RNA polymerase (Pol) III-independent manner and subsequently induces type I interferon (IFN) responses. Knockdown or inhibition of RNA Pol III had no effect on beta interferon (IFN-β) induction by KSHV. By using high-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated by cross-linking immunoprecipitation (HITS-CLIP) approach, we identified multiple KSHV regions that give rise to RNA fragments binding to RIG-I, such as ORF810420-10496, Repeat region (LIR1)119059-119204, and ORF2543561-43650 The sequence dissimilarity between these fragments suggests that RIG-I detects a particular structure rather than a specific sequence motif. Synthesized ORF810420-10496 RNA stimulated RIG-I-dependent but RNA Pol III-independent IFN-β signaling. In summary, several KSHV RNAs are sensed by RIG-I in a RNA Pol III-independent manner.IMPORTANCE Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the causative agent of Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman's disease. Innate immune responses against viral infections, especially the induction of type I interferon, are critical for limiting the replication of viruses. Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I), a cytosolic RNA helicase sensor, plays a significant role in the induction of type I interferon responses following viral infection. Here, we identified multiple RNA regions in KSHV as potential virus ligands that bind to RIG-I and stimulate RIG-I-dependent but RNA Pol III-independent IFN-β signaling. Our results expand the role of RIG-I by providing an example of a DNA virus activating a canonical RNA-sensing pathway.
Keywords: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; RIG-I; innate immunity.
Copyright © 2018 Zhang et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RIG-I like receptor sensing of host RNAs facilitates the cell-intrinsic immune response to KSHV infection.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 19;9(1):4841. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07314-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30451863 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-Dependent Suppression of Type I Interferon Signaling Promotes Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication.J Virol. 2018 Apr 27;92(10):e00078-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00078-18. Print 2018 May 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29514903 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of RIG-I-mediated signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded deubiquitinase ORF64.J Virol. 2011 Oct;85(20):10899-904. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00690-11. Epub 2011 Aug 10. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21835791 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and the innate immune system.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Oct;25(5):597-609. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Jun 21. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 25037686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: a lymphotropic human herpesvirus associated with Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman's disease.Semin Diagn Pathol. 1997 Feb;14(1):54-66. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9044510 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation and Evasion of RLR Signaling by DNA Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 20;12:804511. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.804511. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34987495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus prevents dsRNA formation by promoting efficient splicing of viral RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Feb 22;50(3):1201-1220. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab896. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34671803 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Evasion of RIG-I-Like Receptor-Mediated Immunity through Dysregulation of Ubiquitination and ISGylation.Viruses. 2021 Jan 26;13(2):182. doi: 10.3390/v13020182. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33530371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Lytic KSHV Infection in Human Endothelial Cells Reveals Targets of Viral Immune Modulation.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108249. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108249. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053346 Free PMC article.
-
Species-Specific Deamidation of RIG-I Reveals Collaborative Action between Viral and Cellular Deamidases in HSV-1 Lytic Replication.mBio. 2021 Mar 30;12(2):e00115-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00115-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33785613 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
