Global Burden of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in People Living With HIV: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 29967196
- PMCID: PMC6221183
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.033369
Global Burden of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in People Living With HIV: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: With advances in antiretroviral therapy, most deaths in people with HIV are now attributable to noncommunicable illnesses, especially cardiovascular disease. We determine the association between HIV and cardiovascular disease, and estimate the national, regional, and global burden of cardiovascular disease attributable to HIV.
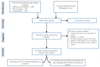
Methods: We conducted a systematic review across 5 databases from inception to August 2016 for longitudinal studies of cardiovascular disease in HIV infection. A random-effects meta-analysis across 80 studies was used to derive the pooled rate and risk of cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV. We then estimated the temporal changes in the population-attributable fraction and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) from HIV-associated cardiovascular disease from 1990 to 2015 at a regional and global level. National cardiovascular DALYs associated with HIV for 2015 were derived for 154 of the 193 United Nations member states. The main outcome measure was the pooled estimate of the rate and risk of cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV and the national, regional, and global estimates of DALYs from cardiovascular disease associated with HIV.
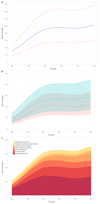
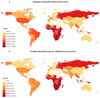
Results: In 793 635 people living with HIV and a total follow-up of 3.5 million person-years, the crude rate of cardiovascular disease was 61.8 (95% CI, 45.8-83.4) per 10 000 person-years. In comparison with individuals without HIV, the risk ratio for cardiovascular disease was 2.16 (95% CI, 1.68-2.77). Over the past 26 years, the global population-attributable fraction from cardiovascular disease attributable to HIV increased from 0.36% (95% CI, 0.21%-0.56%) to 0.92% (95% CI, 0.55%-1.41%), and DALYs increased from 0.74 (95% CI, 0.44-1.16) to 2.57 (95% CI, 1.53-3.92) million. There was marked regional variation with most DALYs lost in sub-Saharan Africa (0.87 million, 95% CI, 0.43-1.70) and the Asia Pacific (0.39 million, 95% CI, 0.23-0.62) regions. The highest population-attributable fraction and burden were observed in Swaziland, Botswana, and Lesotho.
Conclusions: People living with HIV are twice as likely to develop cardiovascular disease. The global burden of HIV-associated cardiovascular disease has tripled over the past 2 decades and is now responsible for 2.6 million DALYs per annum with the greatest impact in sub-Saharan Africa and the Asia Pacific regions.
Clinical trial registration: URL: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero . Unique identifier: CRD42016048257.
Keywords: HIV; cardiovascular diseases; global burden of disease; myocardial infarction; stroke.
Figures

Comment in
-
Time to Recognize HIV Infection as a Major Cardiovascular Risk Factor.Circulation. 2018 Sep 11;138(11):1113-1115. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036211. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 30354392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Global and Regional Estimate of HIV-Associated Stroke Burden: A Meta-Analysis and Population Attributable Modeling Study.Stroke. 2023 Sep;54(9):2390-2400. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.123.043410. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Stroke. 2023. PMID: 37477007
-
Global burden of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in people with hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and modelling study.Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct;4(10):794-804. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30227-4. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31377134 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the burden of disease attributable to injecting drug use as a risk factor for HIV, hepatitis C, and hepatitis B: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Dec;16(12):1385-1398. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)30325-5. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27665254
-
Global burden of disease attributable to illicit drug use and dependence: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.Lancet. 2013 Nov 9;382(9904):1564-74. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61530-5. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23993281 Review.
-
Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990-2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010.Lancet. 2014 Jan 18;383(9913):245-54. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61953-4. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24449944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of HIV Infection With Cardiovascular Pathology Based on Advanced Cardiovascular Imaging: A Systematic Review.JAMA. 2022 Sep 13;328(10):951-962. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.15078. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 36098725 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of Association of Vascular Risk Factors with HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders in cART-Treated Adults Aged ≥ 50 Years in Tanzania.Viruses. 2024 May 22;16(6):819. doi: 10.3390/v16060819. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38932112 Free PMC article.
-
Statins Utilization in Adults With HIV: The Treatment Gap and Predictors of Statin Initiation.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022 Dec 15;91(5):469-478. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000003083. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2022. PMID: 36053091 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslipidemia among HIV-infected patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08910-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38166636 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk over time among people living with HIV.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024 Apr 2;79(4):897-902. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae049. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38416697
References
-
- Global AIDS update 2016. Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS; 2016. Available from http://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2016/Global-AIDS-update-2016.
-
- Mensah GA, Roth GA, Sampson UK, Moran AE, Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Naghavi M, Murray CJ, Mortality GBD and Causes of Death C Mortality from cardiovascular diseases in sub-Saharan Africa, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis of data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2015;26:S6–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Ortblad KF, Guinovart C, Lim SS, Wolock TM, Roberts DA, Dansereau EA, Graetz N, Barber RM, Brown JC, Wang H, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality for HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria during 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014;384:1005–1070. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, Aschman DJ, Holmberg SD. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

