The role of radiology in the evaluation of the immunotherapy efficacy
- PMID: 29951295
- PMCID: PMC5994498
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2018.05.130
The role of radiology in the evaluation of the immunotherapy efficacy
Abstract
In the last years, a great interest has arisen on immunotherapy for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Check-point inhibitor drugs are now considered clinical practice standard in different settings and their use is expected to increase significantly in the near future. As treatment options for lung cancer advance and vary, the different patterns of radiological response increase in number and heterogeneity. To correctly evaluate the radiological findings after and during these treatments is of paramount importance, both in the clinical and sperimental setting. In consideration of their peculiar mechanism, immunotherapies can determine unusual response patterns on imaging, that cannot be correctly evaluated with the traditional response criteria such as World Health Organization (WHO) and Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumours (RECIST). Therefore, during these years, several response criteria [immune-related response criteria (irRC), irRECIST and iRECIST] were proposed and applied in clinical trials on immunotherapies. The aim of this review is to describe the radiological findings after immunotherapy, to critically discuss the different response criteria and the imaging of immune-related adverse events.
Keywords: Lung cancer; adverse events; immunotherapy; radiology; response criteria.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
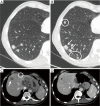
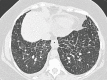
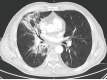
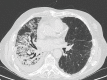
Similar articles
-
Immunotherapy and the role of imaging.Cancer. 2018 Jul 15;124(14):2906-2922. doi: 10.1002/cncr.31349. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29671876 Review.
-
Response evaluation for immunotherapy through semi-automatic software based on RECIST 1.1, irRC, and iRECIST criteria: comparison with subjective assessment.Acta Radiol. 2020 Jul;61(7):983-991. doi: 10.1177/0284185119887588. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Acta Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31739675
-
Patterns of responses in metastatic NSCLC during PD-1 or PDL-1 inhibitor therapy: Comparison of RECIST 1.1, irRECIST and iRECIST criteria.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Jan;88:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.10.017. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29182990
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Assessment of the performance and the agreement of iRECIST, irRC, and irRECIST.J Cancer Res Ther. 2024 Jan 1;20(1):156-162. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1898_22. Epub 2023 Apr 7. J Cancer Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38554314
-
Response criteria for immunotherapy and the radiologic patterns of immune-related adverse events.Eur J Radiol. 2022 Jan;146:110062. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2021.110062. Epub 2021 Nov 20. Eur J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34890935 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing Radiological Response to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: An Evolving Arena.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2024 Jan 3;4(1):1-8. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10278. eCollection 2024 Jan-Feb. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2024. PMID: 38173660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early objective response to avelumab treatment is associated with improved overall survival in patients with metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Apr;68(4):609-618. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-02295-4. Epub 2019 Feb 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30721341 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abdominal CT manifestations of adverse events to immunotherapy: a primer for radiologists.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020 Sep;45(9):2624-2636. doi: 10.1007/s00261-020-02531-5. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020. PMID: 32451672 Review.
-
The radiological appearances of lung cancer treated with immunotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2023 Mar 1;96(1144):20210270. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210270. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36367539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are radiologists ready to evaluate true response to immunotherapy?Insights Imaging. 2021 Feb 24;12(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-00968-w. Insights Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33625595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nivolumab Approved for Lung Cancer Cancer Discov 2015;5:OF1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
