The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins
- PMID: 2988123
- PMCID: PMC4450672
- DOI: 10.1126/science.2988123
The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins
Abstract
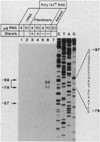
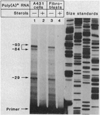
The multifunctional nature of coated pit receptors predicts that these proteins will contain multiple domains. To establish the genetic basis for these domains (LDL) receptor. This gene is more than 45 kilobases in length and contains 18 exons, most of which correlate with functional domains previously defined at the protein level. Thirteen of the 18 exons encode protein sequences that are homologous to sequences in other proteins: five of these exons encode a sequence similar to one in the C9 component of complement; three exons encode a sequence similar to a repeat sequence in the precursor for epidermal growth factor (EGF) and in three proteins of the blood clotting system (factor IX, factor X, and protein C); and five other exons encode nonrepeated sequences that are shared only with the EGF precursor. The LDL receptor appears to be a mosaic protein built up of exons shared with different proteins, and it therefore belongs to several supergene families.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cassette of eight exons shared by genes for LDL receptor and EGF precursor.Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):893-5. doi: 10.1126/science.3873704. Science. 1985. PMID: 3873704
-
Deletion of exon encoding cysteine-rich repeat of low density lipoprotein receptor alters its binding specificity in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia.J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13114-20. J Biol Chem. 1986. PMID: 3020025
-
Two novel point mutations in the EGF precursor homology domain of the LDL receptor gene causing familial hypercholesterolemia.Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;96(2):241-2. doi: 10.1007/BF00207391. Hum Genet. 1995. PMID: 7635482
-
Structure of the gene for cartilage matrix protein, a modular protein of the extracellular matrix. Exon/intron organization, unusual splice sites, and relation to alpha chains of beta 2 integrins, von Willebrand factor, complement factors B and C2, and epidermal growth factor.J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8126-34. J Biol Chem. 1989. PMID: 2542265
-
Two novel frameshift mutations associated with the presence of direct repeats of the LDL receptor gene in familial hypercholesterolemia.Hum Genet. 1993 Oct;92(4):331-5. doi: 10.1007/BF01247329. Hum Genet. 1993. PMID: 8225312
Cited by
-
Proteolytic processing of the 600 kd low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) occurs in a trans-Golgi compartment.EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1769-76. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08301.x. EMBO J. 1990. PMID: 2112085 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Signaling Mediated by ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 in Human Neurons Parallels Alzheimer's Disease Risk.J Neurosci. 2019 Sep 11;39(37):7408-7427. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2994-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jul 22. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31331998 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation scanning by meltMADGE: validations using BRCA1 and LDLR, and demonstration of the potential to identify severe, moderate, silent, rare, and paucimorphic mutations in the general population.Genome Res. 2005 Jul;15(7):967-77. doi: 10.1101/gr.3313405. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 15998910 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the Genetic Relationship between Atherosclerosis and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Biological Interaction Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 18;24(4):4124. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044124. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835545 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis lesions in rabbits with deficiency of low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) on exon 7.EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.020. Epub 2018 Sep 19. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30243490 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

