ZNF423: A New Player in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29867779
- PMCID: PMC5968090
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00255
ZNF423: A New Player in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
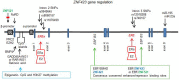
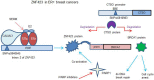
Preventive therapy can target hormone-responsive breast cancer (BC) by treatment with selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and reduce the incidence of BC. Genome-wide association studies have identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with relevant predictive values, SNPs in the ZNF423 gene were associated with decreased risk of BC during SERM therapy, and SNPs in the Cathepsin O gene with an increased risk. ZNF423, which was not previously associated with BC is a multifunctional transcription factor known to have a role in development, neurogenesis, and adipogenesis and is implicated in other types of cancer. ZNF423 is transcriptionally controlled by the homolog ZNF521, early B cell factor transcription factor, epigenetic silencing of the promoter by CpG island hyper-methylation, and also by ZNF423 itself in an auto-regulatory loop. In BC cells, ZNF423 expression is found to be induced by estrogen, dependent on the binding of the estrogen receptor and calmodulin-like 3 to SNPs in ZNP423 intronic sites in proximity to consensus estrogen response elements. ZNF423 has also been shown to play a mechanistic role by trans-activating the tumor suppressor BRCA1 and thus modulating the DNA damage response. Even though recent extensive trial studies did not classify these SNPs with the highest predictive values, for inclusion in polygenic SNP analysis, the mechanism unveiled in these studies has introduced ZNF423 as a factor important in the control of the estrogen response. Here, we aim at providing an overview of ZNF423 expression and functional role in human malignancies, with a specific focus on its implication in hormone-responsive BC.
Keywords: ZNF423; ZNF521; breast cancer; calmodulin like 3; cathepsin O; estrogen receptors; selective estrogen receptor modulators; single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calmodulin-like protein 3 is an estrogen receptor alpha coregulator for gene expression and drug response in a SNP, estrogen, and SERM-dependent fashion.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 18;19(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0890-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28821270 Free PMC article.
-
Selective estrogen receptor modulators and pharmacogenomic variation in ZNF423 regulation of BRCA1 expression: individualized breast cancer prevention.Cancer Discov. 2013 Jul;3(7):812-25. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0038. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Cancer Discov. 2013. PMID: 23764426 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer chemoprevention pharmacogenomics: Deep sequencing and functional genomics of the ZNF423 and CTSO genes.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2017 Aug 21;3:30. doi: 10.1038/s41523-017-0036-4. eCollection 2017. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28856246 Free PMC article.
-
Selective estrogen-receptor modulators and antihormonal resistance in breast cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2007 Dec 20;25(36):5815-24. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.3886. Epub 2007 Sep 24. J Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17893378 Review.
-
Clinical use of selective estrogen receptor modulators and down regulators with the main focus on breast cancer.Minerva Ginecol. 2009 Dec;61(6):517-39. Minerva Ginecol. 2009. PMID: 19942839 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Role of microRNAs Targeting the Transcription Co-Factor ZNF521 in Normal Tissues and Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 6;22(16):8461. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168461. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of TTC17 promotes breast cancer metastasis through RAP1/CDC42 signaling and sensitizes it to rapamycin and paclitaxel.Cell Biosci. 2023 Mar 9;13(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01004-8. Cell Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36895029 Free PMC article.
-
The stem cell-associated transcription co-factor, ZNF521, interacts with GLI1 and GLI2 and enhances the activity of the Sonic hedgehog pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Sep 26;10(10):715. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1946-x. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31558698 Free PMC article.
-
Lipedema: Insights into Morphology, Pathophysiology, and Challenges.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 30;10(12):3081. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123081. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Zinc Finger Protein 423 in Proliferation and Invasion of Cholangiocarcinoma through Oxidative Stress.Biomolecules. 2019 Jul 7;9(7):263. doi: 10.3390/biom9070263. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31284679 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

