Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development
- PMID: 29799838
- PMCID: PMC5991768
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007412
Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development
Abstract
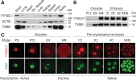
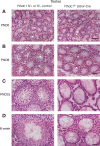
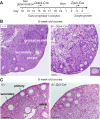
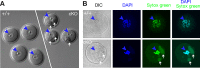
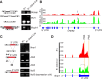
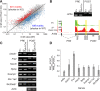
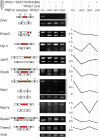
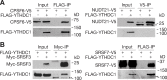
The N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification is the most prevalent internal RNA modification in eukaryotes. The majority of m6A sites are found in the last exon and 3' UTRs. Here we show that the nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 is essential for embryo viability and germline development in mouse. Specifically, YTHDC1 is required for spermatogonial development in males and for oocyte growth and maturation in females; Ythdc1-deficient oocytes are blocked at the primary follicle stage. Strikingly, loss of YTHDC1 leads to extensive alternative polyadenylation in oocytes, altering 3' UTR length. Furthermore, YTHDC1 deficiency causes massive alternative splicing defects in oocytes. The majority of splicing defects in mutant oocytes are rescued by introducing wild-type, but not m6A-binding-deficient, YTHDC1. YTHDC1 is associated with the pre-mRNA 3' end processing factors CPSF6, SRSF3, and SRSF7. Thus, YTHDC1 plays a critical role in processing of pre-mRNA transcripts in the oocyte nucleus and may have similar non-redundant roles throughout fetal development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear m6 A reader YTHDC1 suppresses proximal alternative polyadenylation sites by interfering with the 3' processing machinery.EMBO Rep. 2022 Nov 7;23(11):e54686. doi: 10.15252/embr.202254686. Epub 2022 Sep 12. EMBO Rep. 2022. PMID: 36094741 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs.Elife. 2017 Oct 6;6:e31311. doi: 10.7554/eLife.31311. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28984244 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear m(6)A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing.Mol Cell. 2016 Feb 18;61(4):507-519. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.01.012. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26876937
-
m(6)A: Signaling for mRNA splicing.RNA Biol. 2016 Sep;13(9):756-9. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1201628. Epub 2016 Jun 28. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 27351695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted effects of YTHDC1-mediated nuclear m6A recognition.Trends Genet. 2022 Apr;38(4):325-332. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 34920906 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of YTH domain-containing genes, encoding the m6A readers, and their expression in tomato.Plant Cell Rep. 2021 Jul;40(7):1229-1245. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02716-2. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Plant Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34081180
-
Epigenetic regulations in mammalian spermatogenesis: RNA-m6A modification and beyond.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jun;78(11):4893-4905. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03823-9. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33835194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in acute myeloid leukemia.Biomark Res. 2021 May 17;9(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00293-w. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34001273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates the scaffold function of LINE1 RNA in mouse ESCs and early embryos.Protein Cell. 2021 Jun;12(6):455-474. doi: 10.1007/s13238-021-00837-8. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Protein Cell. 2021. PMID: 33886094 Free PMC article.
-
Reading the m6A-encoded epitranscriptomic information in development and diseases.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 28;14(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01293-7. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39342406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Machnicka MA, Milanowska K, Osman Oglou O, Purta E, Kurkowska M, et al. (2013) MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways—2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res 41: D262–7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR. (2014) The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15: 313–326. doi: 10.1038/nrm3785 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yue Y, Liu J, He C. (2015) RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev 29: 1343–1355. doi: 10.1101/gad.262766.115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu N, Pan T. (2016) N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat Struct Mol Biol 23: 98–102. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3162 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, et al. (2012) Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 149: 1635–1646. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

