Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism
- PMID: 29789545
- PMCID: PMC5993786
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8
Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism
Abstract
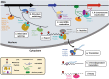
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is a chemical modification present in multiple RNA species, being most abundant in mRNAs. Studies on enzymes or factors that catalyze, recognize, and remove m6A have revealed its comprehensive roles in almost every aspect of mRNA metabolism, as well as in a variety of physiological processes. This review describes the current understanding of the m6A modification, particularly the functions of its writers, erasers, readers in RNA metabolism, with an emphasis on its role in regulating the isoform dosage of mRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
m6A readers, writers, erasers, and the m6A epitranscriptome in breast cancer.J Mol Endocrinol. 2022 Dec 21;70(2):e220110. doi: 10.1530/JME-22-0110. Print 2023 Feb 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36367225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 May;15(5):313-26. doi: 10.1038/nrm3785. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24713629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The detection and functions of RNA modification m6A based on m6A writers and erasers.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100973. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100973. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34280435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The m6A landscape of polyadenylated nuclear (PAN) RNA and its related methylome in the context of KSHV replication.RNA. 2021 Sep;27(9):1102-1125. doi: 10.1261/rna.078777.121. Epub 2021 Jun 29. RNA. 2021. Retraction in: RNA. 2022 Feb;28(2):274. doi: 10.1261/rna.079042.121 PMID: 34187903 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A dynamic reversible RNA N6 -methyladenosine modification: current status and perspectives.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):7948-7956. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28014. Epub 2019 Jan 15. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30644095 Review.
Cited by
-
m6ATM: a deep learning framework for demystifying the m6A epitranscriptome with Nanopore long-read RNA-seq data.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Sep 23;25(6):bbae529. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae529. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39438075 Free PMC article.
-
N6 -methyladenosine Steers RNA Metabolism and Regulation in Cancer.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Jul;41(7):538-559. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12161. Epub 2021 May 6. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33955720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jack of all trades? The versatility of RNA in DNA double-strand break repair.Essays Biochem. 2020 Oct 26;64(5):721-735. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200008. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32618336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ALKBH5-Mediated m6A Modification Drives Apoptosis in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Negatively Regulating MUC1.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 22. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01250-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39172331
-
m6A-SAC-seq for quantitative whole transcriptome m6A profiling.Nat Protoc. 2023 Feb;18(2):626-657. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00765-9. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Nat Protoc. 2023. PMID: 36434097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu N, Pan T. N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016;23:98–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

