A20 critically controls microglia activation and inhibits inflammasome-dependent neuroinflammation
- PMID: 29789522
- PMCID: PMC5964249
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04376-5
A20 critically controls microglia activation and inhibits inflammasome-dependent neuroinflammation
Abstract
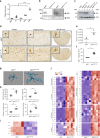
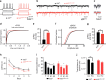
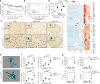
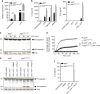
Microglia, the mononuclear phagocytes of the central nervous system (CNS), are important for the maintenance of CNS homeostasis, but also critically contribute to CNS pathology. Here we demonstrate that the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) regulatory protein A20 is crucial in regulating microglia activation during CNS homeostasis and pathology. In mice, deletion of A20 in microglia increases microglial cell number and affects microglial regulation of neuronal synaptic function. Administration of a sublethal dose of lipopolysaccharide induces massive microglia activation, neuroinflammation, and lethality in mice with microglia-confined A20 deficiency. Microglia A20 deficiency also exacerbates multiple sclerosis (MS)-like disease, due to hyperactivation of the Nlrp3 inflammasome leading to enhanced interleukin-1β secretion and CNS inflammation. Finally, we confirm a Nlrp3 inflammasome signature and IL-1β expression in brain and cerebrospinal fluid from MS patients. Collectively, these data reveal a critical role for A20 in the control of microglia activation and neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HIV-1 Tat Primes and Activates Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 29;37(13):3599-3609. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3045-16.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 7. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28270571 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial NLRP3 inflammasome activation in multiple sclerosis.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;119:247-308. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 31997770 Review.
-
NF-κB/ROS and ERK pathways regulate NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Listeria monocytogenes infected BV2 microglia cells.J Microbiol. 2021 Aug;59(8):771-781. doi: 10.1007/s12275-021-0692-9. Epub 2021 Jun 1. J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34061343
-
Leishmania donovani inhibits inflammasome-dependent macrophage activation by exploiting the negative regulatory proteins A20 and UCP2.FASEB J. 2017 Nov;31(11):5087-5101. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700407R. Epub 2017 Aug 1. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28765172
-
Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: Its Role in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2020 Nov;45(11):2560-2572. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03121-z. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 32929691 Review.
Cited by
-
The Gut-Microglia Connection: Implications for Central Nervous System Diseases.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 5;9:2325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02325. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30344525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VSIG4 mediates transcriptional inhibition of Nlrp3 and Il-1β in macrophages.Sci Adv. 2019 Jan 9;5(1):eaau7426. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau7426. eCollection 2019 Jan. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 30662948 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA miR-27b-3p regulate microglial inflammation response and cell apoptosis by inhibiting A20 (TNF-α-induced protein 3).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):9902-9913. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1969195. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34895052 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV1 channel mediates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent neuroinflammation in microglia.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Dec 14;12(12):1159. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04450-9. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34907173 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory signaling pathways in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease with inhibitors, natural products and metabolites (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Nov;52(5):111. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5314. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37800614 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

