S55746 is a novel orally active BCL-2 selective and potent inhibitor that impairs hematological tumor growth
- PMID: 29732004
- PMCID: PMC5929447
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24744
S55746 is a novel orally active BCL-2 selective and potent inhibitor that impairs hematological tumor growth
Abstract
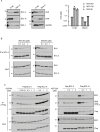
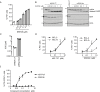
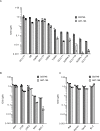
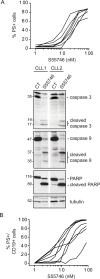
Escape from apoptosis is one of the major hallmarks of cancer cells. The B-cell Lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) gene family encodes pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins that are key regulators of the apoptotic process. Overexpression of the pro-survival member BCL-2 is a well-established mechanism contributing to oncogenesis and chemoresistance in several cancers, including lymphoma and leukemia. Thus, BCL-2 has become an attractive target for therapeutic strategy in cancer, as demonstrated by the recent approval of ABT-199 (Venclexta™) in relapsed or refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with 17p deletion. Here, we describe a novel orally bioavailable BCL-2 selective and potent inhibitor called S55746 (also known as BCL201). S55746 occupies the hydrophobic groove of BCL-2. Its selectivity profile demonstrates no significant binding to MCL-1, BFL-1 (BCL2A1/A1) and poor affinity for BCL-XL. Accordingly, S55746 has no cytotoxic activity on BCL-XL-dependent cells, such as platelets. In a panel of hematological cell lines, S55746 induces hallmarks of apoptosis including externalization of phosphatidylserine, caspase-3 activation and PARP cleavage. Ex vivo, S55746 induces apoptosis in the low nanomolar range in primary Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Mantle Cell Lymphoma patient samples. Finally, S55746 administered by oral route daily in mice demonstrated robust anti-tumor efficacy in two hematological xenograft models with no weight lost and no change in behavior. Taken together, these data demonstrate that S55746 is a novel, well-tolerated BH3-mimetic targeting selectively and potently the BCL-2 protein.
Keywords: BCL-2; BH3-mimetics; apoptosis; hematological malignancies; inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST P Casara and JA Hickman are former employees of Institut de Recherches Servier. M Chanrion, A Claperon, F Colland, O Geneste, AM Girard, F Gravé, G Guasconi, JM Henlin, G Le Toumelin-Braizat, G Lysiak-Auvity, F Rocchetti, E Schneider, JB Starck and A Studeny are full-time employees of Institut de Recherches Servier. T Le Diguarher is a full-time employee of Technology Servier. A Bruno and L Kraus-Berthier are full-time employees of Institut de Recherches Internationales Servier. E Morris, S Qiu and Y Wang are full-time employees of Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research; E Morris and Y Wang are stock owner of Novartis. S LeGouill has served on advisory board for Servier. Amiot and Cohen's laboratories have received research funds from Servier. I Chen, J Davidson, P Dokurno, C Graham, N Matassova, J Murray, C Pedder, N Whitehead, M Wood are full-time employees of Vernalis Ltd. R Hubbard is a part-time employee of Vernalis Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BH3-only proteins are dispensable for apoptosis induced by pharmacological inhibition of both MCL-1 and BCL-XL.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jun;26(6):1037-1047. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0183-7. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30185825 Free PMC article.
-
Binding affinity of pro-apoptotic BH3 peptides for the anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 and A1 proteins: Molecular dynamics simulations of Mcl-1 and A1 in complex with six different BH3 peptides.J Mol Graph Model. 2017 May;73:115-128. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.12.006. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Mol Graph Model. 2017. PMID: 28279820
-
ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor.Cancer Res. 2008 May 1;68(9):3421-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5836. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18451170
-
Therapeutics targeting Bcl-2 in hematological malignancies.Biochem J. 2017 Oct 23;474(21):3643-3657. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170080. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 29061914 Review.
-
Selective Bcl-2 inhibition to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2014 Apr;12(4):224-9. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25003352 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical, Physical and Biological Triggers of Evolutionary Conserved Bcl-xL-Mediated Apoptosis.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 25;12(6):1694. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061694. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630560 Free PMC article.
-
Patent landscape of inhibitors and PROTACs of the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022 Sep;32(9):1003-1026. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2022.2116311. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2022. PMID: 35993382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishing Drug Discovery and Identification of Hit Series for the Anti-apoptotic Proteins, Bcl-2 and Mcl-1.ACS Omega. 2019 May 23;4(5):8892-8906. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b00611. eCollection 2019 May 31. ACS Omega. 2019. PMID: 31459977 Free PMC article.
-
Bcl-xl as the most promising Bcl-2 family member in targeted treatment of chondrosarcoma.Oncogenesis. 2018 Sep 21;7(9):74. doi: 10.1038/s41389-018-0084-0. Oncogenesis. 2018. PMID: 30242253 Free PMC article.
-
A novel peptide derived from Zingiber cassumunar rhizomes exhibits anticancer activity against the colon adenocarcinoma cells (Caco-2) via the induction of intrinsic apoptosis signaling.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 13;19(6):e0304701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304701. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38870120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC, Croce CM. Cloning of the chromosome breakpoint of neoplastic B cells with the t(14;18) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984;226:1097–9. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, Yunis J, Onorato-Showe L, Erikson J, Nowell PC, Croce CM. Molecular cloning of the chromosomal breakpoint of B-cell lymphomas and leukemias with the t(11;14) chromosome translocation. Science. 1984;224:1403–6. - PubMed
-
- Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A, Adams JM. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:49–63. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

