Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Values and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 29730089
- PMCID: PMC5988947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.03.006
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Values and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) values and all-cause and cause-specific mortality.
Patients and methods: We identified all serum 25(OH)D measurements in adults residing in Olmsted County, Minnesota, between January 1, 2005, and December 31, 2011, through the Rochester Epidemiology Project. All-cause mortality was the primary outcome. Patients were followed up until their last clinical visit as an Olmsted County resident, December 31, 2014, or death. Multivariate analyses were adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, month of measurement, and Charlson comorbidity index score.
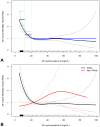
Results: A total of 11,022 individuals had a 25(OH)D measurement between January 1, 2005, and December 31, 2011, with a mean ± SD value of 30.0±12.9 ng/mL. Mean age was 54.3±17.2 years, and most were female (77.1%) and white (87.6%). There were 723 deaths after a median follow-up of 4.8 years (interquartile range, 3.4-6.2 years). Unadjusted all-cause mortality hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% CIs for 25(OH)D values of less than 12, 12 to 19, and more than 50 ng/mL were 2.6 (95% CI, 2.0-3.2), 1.3 (95% CI, 1.0-1.6), and 1.0 (95% CI, 0.72-1.5), respectively, compared with the reference value of 20 to 50 ng/mL. In a multivariate model, the interaction between the effect of 25(OH)D and race/ethnicity on mortality was significant (P<.001). In white patients, adjusted HRs for 25(OH)D values of less than 12, 12 to 19, 20 to 50, and greater than 50 ng/mL were 2.5 (95% CI, 2.2-2.9), 1.4 (95% CI, 1.2-1.6), 1.0 (referent), and 1.0 (95% CI, 0.81-1.3), respectively. In patients of other race/ethnicity, adjusted HRs were 1.9 (95% CI, 1.5-2.3), 1.7 (95% CI, 1.1-2.6), 1.5 (95% CI, 1.0-2.0), and 2.1 (95% CI, 0.77-5.5).
Conclusion: White patients with 25(OH)D values of less than 20 ng/mL had greater all-cause mortality than those with values of 20 to 50 ng/mL, and white patients had greater mortality associated with low 25(OH)D values than patients of other race/ethnicity. Values of 25(OH)D greater than 50 ng/mL were not associated with all-cause mortality.
Copyright © 2018 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
The Death D-fying Vitamin.Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 Jun;93(6):679-681. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.014. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018. PMID: 29866279 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D values and risk of incident cardiovascular disease: A population-based retrospective cohort study.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Oct;213:105953. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105953. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34274459 Free PMC article.
-
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Subsequent Cancer Incidence and Mortality: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study.Mayo Clin Proc. 2021 Aug;96(8):2157-2167. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.037. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021. PMID: 34353470 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and individual-level socioeconomic status.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;197:105545. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105545. Epub 2019 Nov 18. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31751783 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of 25-hydroxyvitamin D values and risk of fracture: a population-based retrospective cohort study.Osteoporos Int. 2020 Sep;31(9):1787-1799. doi: 10.1007/s00198-020-05436-7. Epub 2020 May 6. Osteoporos Int. 2020. PMID: 32377805 Free PMC article.
-
Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are inversely associated with all-cause mortality among Koreans: a nationwide cohort study.Nutr Res. 2023 May;113:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2023.02.008. Epub 2023 Mar 5. Nutr Res. 2023. PMID: 37028268
Cited by
-
Editorial: Classic and Pleiotropic Actions of Vitamin D.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 May 29;10:341. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00341. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31191460 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Principal results of the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) and updated meta-analyses of relevant vitamin D trials.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Apr;198:105522. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105522. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31733345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Vitamin D prescribing practices among clinical practitioners during the COVID-19 pandemic.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 11;5(4):e691. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.691. eCollection 2022 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35844828 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Rheumatic Diseases: A Review of Clinical Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 1;22(19):10659. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910659. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D and Its Potential Benefit for the COVID-19 Pandemic.Endocr Pract. 2021 May;27(5):484-493. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Endocr Pract. 2021. PMID: 33744444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(3):266–281. - PubMed
-
- Durup D, Jorgensen HL, Christensen J, Schwarz P, Heegaard AM, Lind B. A reverse J-shaped association of all-cause mortality with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in general practice: the CopD study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(8):2644–2652. - PubMed
-
- Zittermann A, Iodice S, Pilz S, Grant WB, Bagnardi V, Gandini S. Vitamin D deficiency and mortality risk in the general population: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95(1):91–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

