Corosolic Acid Induces Non-Apoptotic Cell Death through Generation of Lipid Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Human Renal Carcinoma Caki Cells
- PMID: 29702597
- PMCID: PMC5983573
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19051309
Corosolic Acid Induces Non-Apoptotic Cell Death through Generation of Lipid Reactive Oxygen Species Production in Human Renal Carcinoma Caki Cells
Abstract
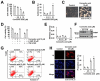
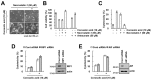
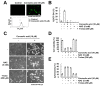
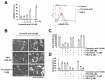
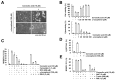
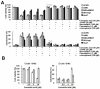
Corosolic acid is one of the pentacyclic triterpenoids isolated from Lagerstroemia speciose and has been reported to exhibit anti-cancer and anti-proliferative activities in various cancer cells. In the present study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms of corosolic acid in cancer cell death. Corosolic acid induces a decrease of cell viability and an increase of cell cytotoxicity in human renal carcinoma Caki cells. Corosolic acid-induced cell death is not inhibited by apoptosis inhibitor (z-VAD-fmk, a pan-caspase inhibitor), necroptosis inhibitor (necrostatin-1), or ferroptosis inhibitors (ferrostatin-1 and deferoxamine (DFO)). Furthermore, corosolic acid significantly induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, but antioxidants (N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) and trolox) do not inhibit corosolic acid-induced cell death. Interestingly, corosolic acid induces lipid oxidation, and α-tocopherol markedly prevents corosolic acid-induced lipid peroxidation and cell death. Anti-chemotherapeutic effects of α-tocopherol are dependent on inhibition of lipid oxidation rather than inhibition of ROS production. In addition, corosolic acid induces non-apoptotic cell death in other renal cancer (ACHN and A498), breast cancer (MDA-MB231), and hepatocellular carcinoma (SK-Hep1 and Huh7) cells, and α-tocopherol markedly inhibits corosolic acid-induced cell death. Therefore, our results suggest that corosolic acid induces non-apoptotic cell death in cancer cells through the increase of lipid peroxidation.
Keywords: corosolic acid; lipid ROS; non-apoptotic cell death; α-tocopherol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corosolic acid induces apoptotic cell death in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells in vitro.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jun;56:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 20. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23454206
-
RIP1-dependent reactive oxygen species production executes artesunate-induced cell death in renal carcinoma Caki cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Nov;435(1-2):15-24. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3052-7. Epub 2017 May 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28466458
-
Lipoxygenase inhibitors protect acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells from ferroptotic cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;140:41-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.06.112. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28595877
-
A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid.Phytother Res. 2012 Mar;26(3):317-24. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3664. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 22095937 Review.
-
GPx4, Lipid Peroxidation, and Cell Death: Discoveries, Rediscoveries, and Open Issues.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jul 1;29(1):61-74. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7115. Epub 2017 May 30. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28462584 Review.
Cited by
-
Corosolic acid isolated from Eriobotrya japonica leaves reduces glucose level in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells, zebrafish and rats.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 13;9(1):4388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40934-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30867526 Free PMC article.
-
Floral Elegance Meets Medicinal Marvels: Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of the Genus Lagerstroemia L.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 28;13(21):3016. doi: 10.3390/plants13213016. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39519935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular subtypes based on ferroptosis-related genes and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in lung adenocarcinoma.Oncoimmunology. 2021 Sep 11;10(1):1959977. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2021.1959977. eCollection 2021. Oncoimmunology. 2021. PMID: 34527427 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable methods for the carboxymethylation and methylation of ursolic acid with dimethyl carbonate under mild and acidic conditions.RSC Adv. 2024 May 24;14(24):16921-16934. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02122c. eCollection 2024 May 22. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38799212 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Thienopyrimidine-Hydrazinyl Compounds Induce DRP1-Mediated Non-Apoptotic Cell Death in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;16(15):2621. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152621. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devasagayam T.P., Tilak J.C., Boloor K.K., Sane K.S., Ghaskadbi S.S., Lele R.D. Free radicals and antioxidants in human health: Current status and future prospects. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 2004;52:794–804. - PubMed
-
- Bielski B.H., Arudi R.L., Sutherland M.W. A study of the reactivity of HO2/O2- with unsaturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1983;258:4759–4761. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

