The binding of an anti-PD-1 antibody to FcγRΙ has a profound impact on its biological functions
- PMID: 29687231
- PMCID: PMC6006217
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-018-2160-x
The binding of an anti-PD-1 antibody to FcγRΙ has a profound impact on its biological functions
Abstract
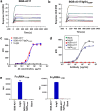
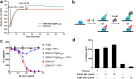
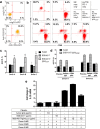
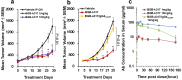
Antibodies targeting PD-1 have been demonstrated durable anti-cancer activity in certain cancer types. However, the anti-PD-1 antibodies are less or not efficacious in many situations, which might be attributed to co-expression of multiple inhibitory receptors or presence of immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. Most of the anti-PD-1 antibodies used in clinical studies are of IgG4 isotype with the S228P mutation (IgG4S228P). The functional impact by the interaction of anti-PD-1 IgG4S228P antibody with Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs) is poorly understood. To assess the effects, we generated a pair of anti-PD-1 antibodies: BGB-A317/IgG4S228P and BGB-A317/IgG4-variant (abbreviated as BGB-A317), with the same variable regions but two different IgG4 Fc-hinge sequences. There was no significant difference between these two antibodies in binding to PD-1. However, BGB-A317/IgG4S228P binds to human FcγRI with high affinity and mediates crosslinking between PD-1 and FcγRI. In contrast, BGB-A317 does neither. Further cell-based assays showed that such crosslinking could reverse the function of an anti-PD-1 antibody from blocking to activating. More importantly, the crosslinking induces FcγRI+ macrophages to phagocytose PD-1+ T cells. In a mouse model transplanted with allogeneic human cancer cells and PBMCs, BGB-A317 showed significant tumor growth inhibition, whereas BGB-A317/IgG4S228P had no such inhibition. Immunohistochemistry study revealed an inverse correlation between FcγRI+ murine macrophage infiltration and the density of CD8+PD-1+ human T cells within tumors in the BGB-A317/IgG4S228P-treated group. These evidences suggested that FcγRI+ binding and crosslinking had negative impact on the anti-PD-1 antibody-mediated anti-cancer activity.
Keywords: Antibody; Cancer therapy; FcγRI; Macrophages; PD-1.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have ownership interest in BeiGene. Tong Zhang, Lanlan Xu, Qi Liu., Jing Song and Kang Li are inventors on a patent covering BGB-A317 described in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor With a Glyco-Engineered Fc-Region Has Increased Efficacy in Mice With Colitis.Gastroenterology. 2017 Nov;153(5):1351-1362.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.021. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28756234
-
Phosphatidylserine-targeting antibodies augment the anti-tumorigenic activity of anti-PD-1 therapy by enhancing immune activation and downregulating pro-oncogenic factors induced by T-cell checkpoint inhibition in murine triple-negative breast cancers.Breast Cancer Res. 2016 May 11;18(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0708-2. Breast Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27169467 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of MEDI4736, an Antagonistic Anti-PD-L1 Monoclonal Antibody.Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Sep;3(9):1052-62. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0191. Epub 2015 May 5. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25943534
-
The many faces of FcγRI: implications for therapeutic antibody function.Immunol Rev. 2015 Nov;268(1):160-74. doi: 10.1111/imr.12334. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26497519 Review.
-
Therapeutic uses of anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies.Int Immunol. 2015 Jan;27(1):39-46. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxu095. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Int Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25323844 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Combination Therapy With PD-1 Blockade for Acute Myeloid Leukemia After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Resulted in Fatal GVHD.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 1;12:639217. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.639217. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868266 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid Cells as Clinical Biomarkers for Immune Checkpoint Blockade.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 24;11:1590. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01590. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Oct 19;8(4):616. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040616. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33086471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The "Great Debate" at Melanoma Bridge 2020: December, 5th, 2020.J Transl Med. 2021 Apr 7;19(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02808-3. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33827575 Free PMC article.
-
Next generation of anti-PD-L1 Atezolizumab with enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in vivo.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 11;11(1):5774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85329-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33707569 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

