C-Reactive Protein in Atherothrombosis and Angiogenesis
- PMID: 29552019
- PMCID: PMC5840191
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00430
C-Reactive Protein in Atherothrombosis and Angiogenesis
Abstract
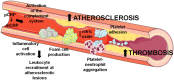
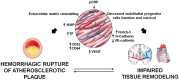
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a short pentraxin mainly found as a pentamer in the circulation, or as non-soluble monomers CRP (mCRP) in tissues, exerting different functions. This review is focused on discussing the role of CRP in cardiovascular disease, including recent advances on the implication of CRP and its forms specifically on the pathogenesis of atherothrombosis and angiogenesis. Besides its role in the humoral innate immune response, CRP contributes to cardiovascular disease progression by recognizing and binding multiple intrinsic ligands. mCRP is not present in the healthy vessel wall but it becomes detectable in the early stages of atherogenesis and accumulates during the progression of atherosclerosis. CRP inhibits endothelial nitric oxide production and contributes to plaque instability by increasing endothelial cell adhesion molecules expression, by promoting monocyte recruitment into the atheromatous plaque and by enzymatically binding to modified low-density lipoprotein. CRP also contributes to thrombosis, but depending on its form it elicits different actions. Pentameric CRP has no involvement in thrombogenesis, whereas mCRP induces platelet activation and thrombus growth. In addition, mCRP has apparently contradictory pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic effects determining tissue remodeling in the atherosclerotic plaque and in infarcted tissues. Overall, CRP contributes to cardiovascular disease by several mechanisms that deserve an in-depth analysis.
Keywords: angiogenesis; atherosclerosis; c-reactive protein; cardiovascular disease; ischemic heart disease; monomeric C-reactive protein; pentameric C-reactive protein; thrombosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A role for monomeric C-reactive protein in regulation of angiogenesis, endothelial cell inflammation and thrombus formation in cardiovascular/cerebrovascular disease?Histol Histopathol. 2009 Nov;24(11):1473-8. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.1473. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19760596 Review.
-
Current Position on the Role of Monomeric C-reactive Protein in Vascular Pathology and Atherothrombosis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(1):37-43. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191216144055. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 31840602 Review.
-
mCRP triggers angiogenesis by inducing F3 transcription and TF signalling in microvascular endothelial cells.Thromb Haemost. 2017 Jan 26;117(2):357-370. doi: 10.1160/TH16-07-0524. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Thromb Haemost. 2017. PMID: 27808345
-
Dissociation of pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein on activated platelets localizes inflammation to atherosclerotic plaques.Circ Res. 2009 Jul 17;105(2):128-37. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.190611. Epub 2009 Jun 11. Circ Res. 2009. PMID: 19520972
-
A redox switch in C-reactive protein modulates activation of endothelial cells.FASEB J. 2011 Sep;25(9):3186-96. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-182741. Epub 2011 Jun 13. FASEB J. 2011. PMID: 21670067
Cited by
-
Association between inflammatory obesity phenotypes, FTO-rs9939609, and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Res Med Sci. 2020 May 22;25:46. doi: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_429_19. eCollection 2020. J Res Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32765616 Free PMC article.
-
Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaque: Is There a Molecular Signature?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 7;23(21):13638. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113638. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Blood C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients With Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2019 Sep 18;10:974. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00974. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31620066 Free PMC article.
-
The characteristics of risk factors in Chinese young women with acute coronary syndrome.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Jun 12;20(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01577-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32532208 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Model for Analysing the Role of Shear Stress in Angiogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7886. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097886. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175591 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiele JR, Habersberger J, Braig D, Schmidt Y, Goerendt K, Maurer V, et al. Dissociation of pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein localizes and aggravates inflammation: in vivo proof of a powerful proinflammatory mechanism and a new anti-inflammatory strategy. Circulation (2014) 130:35–50.10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.007124 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

