Distinct signalling properties of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 in mediating insulin/IGF-1 action
- PMID: 29550500
- PMCID: PMC5951756
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.03.003
Distinct signalling properties of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2 in mediating insulin/IGF-1 action
Abstract
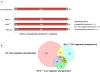
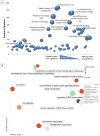
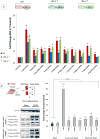
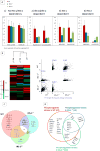
Insulin/IGF-1 action is driven by a complex and highly integrated signalling network. Loss-of-function studies indicate that the major insulin/IGF-1 receptor substrate (IRS) proteins, IRS-1 and IRS-2, mediate different biological functions in vitro and in vivo, suggesting specific signalling properties despite their high degree of homology. To identify mechanisms contributing to the differential signalling properties of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in the mediation of insulin/IGF-1 action, we performed comprehensive mass spectrometry (MS)-based phosphoproteomic profiling of brown preadipocytes from wild type, IRS-1-/- and IRS-2-/- mice in the basal and IGF-1-stimulated states. We applied stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) for the accurate quantitation of changes in protein phosphorylation. We found ~10% of the 6262 unique phosphorylation sites detected to be regulated by IGF-1. These regulated sites included previously reported substrates of the insulin/IGF-1 signalling pathway, as well as novel substrates including Nuclear Factor I X and Semaphorin-4B. In silico prediction suggests the protein kinase B (PKB), protein kinase C (PKC), and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) as the main mediators of these phosphorylation events. Importantly, we found preferential phosphorylation patterns depending on the presence of either IRS-1 or IRS-2, which was associated with specific sets of kinases involved in signal transduction downstream of these substrates such as PDHK1, MAPK3, and PKD1 for IRS-1, and PIN1 and PKC beta for IRS-2. Overall, by generating a comprehensive phosphoproteomic profile from brown preadipocyte cells in response to IGF-1 stimulation, we reveal both common and distinct insulin/IGF-1 signalling events mediated by specific IRS proteins.
Keywords: Insulin receptor substrate; Insulin/IGF-1; Kinase; Phosphoproteomics; Signal transduction.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased insulin sensitivity in IGF-I receptor--deficient brown adipocytes.Diabetes. 2002 Mar;51(3):743-54. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.3.743. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 11872675
-
Platelet-derived growth factor negatively regulates the insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway through the coordinated action of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and protein kinase C beta I.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1833(6):1367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.019. Epub 2013 Feb 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23481042
-
Activation of IRS-2-mediated signal transduction by IGF-1, but not TGF-alpha or EGF, augments pancreatic beta-cell proliferation.Diabetes. 2002 Apr;51(4):966-76. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.4.966. Diabetes. 2002. PMID: 11916914
-
Regulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2.Diabetologia. 2012 Oct;55(10):2565-2582. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2644-8. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22869320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear IRS-1 and cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2012 Aug;227(8):2992-3000. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24019. J Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22454254 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Afadin is a scaffold protein repressing insulin action via HDAC6 in adipose tissue.EMBO Rep. 2019 Aug;20(8):e48216. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948216. Epub 2019 Jul 2. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31264358 Free PMC article.
-
The Interactions of Insulin and Vitamin A Signaling Systems for the Regulation of Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Metabolism.Cells. 2021 Aug 21;10(8):2160. doi: 10.3390/cells10082160. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gender Differences in Insulin Resistance: New Knowledge and Perspectives.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Sep 27;45(10):7845-7861. doi: 10.3390/cimb45100496. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37886939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Cr-Mo-Cu alloys for clinical implants with osteogenic effect by increasing bone induction, formation and development in a rabbit model.Burns Trauma. 2020 Dec 21;8:tkaa036. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkaa036. eCollection 2020. Burns Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33376752 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the underlying defect in insulin action in type 2 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2021 May;64(5):994-1006. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05415-5. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33730188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev. 2009;30(6):586–623. - PubMed
-
- White MF. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin action. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182(1–2):3–11. - PubMed
-
- Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR. Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(2):85–96. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

