Association of interleukin-6 polymorphisms with obesity or metabolic traits in young Mexican-Americans
- PMID: 29479468
- PMCID: PMC5818745
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.138
Association of interleukin-6 polymorphisms with obesity or metabolic traits in young Mexican-Americans
Abstract
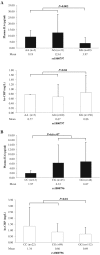
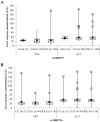
Objective: The objective of the study is to investigate the association of interleukin-6 (IL6) promoter single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs1800797 (-597 G/A) and rs1800796 (-572 G/C) with obesity or metabolic syndrome in Mexican-Americans.
Methods: The rs1800797 and rs1800796 single-nucleotide polymorphisms were genotyped in Mexican-Americans (n = 437) from South Texas, and results were correlated with measures of obesity and metabolic syndrome including body mass index, waist circumference, blood pressure, cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose, liver enzymes, plasma IL6 and high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP).
Results: Significant associations were found for the rs1800796 variant with increased waist circumference, insulin resistance, lower IL6 levels and higher hs-CRP levels. The rs1800797 variant showed no associations with metabolic traits but was associated with higher IL6 levels and lower hs-CRP levels.
Conclusions: Findings in this study support the anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and glucose homeostatic roles of IL6 in Mexican-American youth.
Keywords: Genetics; inflammation; interleukin‐6; obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association study of candidate gene polymorphisms and obesity in a young Mexican-American population from South Texas.Arch Med Res. 2011 Aug;42(6):523-31. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2011.10.010. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Arch Med Res. 2011. PMID: 22056417 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade inflammation markers in children and adolescents: Influence of anthropometric characteristics and CRP and IL6 polymorphisms.Cytokine. 2016 Dec;88:177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 27643980 Clinical Trial.
-
C-reactive protein levels and their relationship with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in Mexican adolescents.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007 Jul;20(7):797-805. doi: 10.1515/jpem.2007.20.7.797. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2007. PMID: 17849742
-
Novel single nucleotide polymorphisms in interleukin 6 affect tacrolimus metabolism in liver transplant patients.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e73405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073405. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2019 Sep 4;14(9):e0222244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222244. PMID: 23991193 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Interleukin-6 polymorphisms are associated with obesity and hyperglycemia in Mexican adolescents.Arch Med Res. 2013 Jan;44(1):62-8. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.10.019. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Arch Med Res. 2013. PMID: 23142265
Cited by
-
Innate-Immunity Genes in Obesity.J Pers Med. 2021 Nov 14;11(11):1201. doi: 10.3390/jpm11111201. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34834553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-6 Polymorphisms Are Not Related to Obesity Parameters in Physically Active Young Men.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 25;12(10):1498. doi: 10.3390/genes12101498. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680892 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Immunometabolic Basis for the Metabolic Syndrome from an Immunonutritional View.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 12;12(8):1825. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081825. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between Interleukin-6 Gene Polymorphism (rs1800795 and rs1800796) and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Ghanaian Population: A Case-Control Study in the Ho Municipality.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Apr 26;2024:3610879. doi: 10.1155/2024/3610879. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38707766 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to liver diseases: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Dec;98(50):e18408. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018408. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31852161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stelzer I, Zelzer S, Raggam RB, et al. Link between leptin and interleukin‐6 levels in the initial phase of obesity related inflammation. Transl Res 2012; 159: 118–124. - PubMed
-
- El‐Wakkad A, Hassan N, Sibaii H, El‐Zayat SR. Proinflammatory, anti‐inflammatory cytokines and adiponkines in students with central obesity. Cytokine 2013; 61: 682–687. - PubMed
-
- Ronti T, Lupattelli G, Mannarino E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: an update. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2006; 64: 355–365. - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA, Jones SA. IL‐6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat Immunol 2015; 16: 448–457. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
