Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions
- PMID: 29472701
- PMCID: PMC5903829
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2017.282
Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions
Abstract
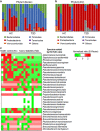
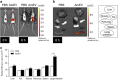
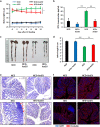
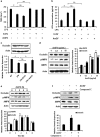
The gut microbiota has an important role in the gut barrier, inflammation and metabolic functions. Studies have identified a close association between the intestinal barrier and metabolic diseases, including obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D). Recently, Akkermansia muciniphila has been reported as a beneficial bacterium that reduces gut barrier disruption and insulin resistance. Here we evaluated the role of A. muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles (AmEVs) in the regulation of gut permeability. We found that there are more AmEVs in the fecal samples of healthy controls compared with those of patients with T2D. In addition, AmEV administration enhanced tight junction function, reduced body weight gain and improved glucose tolerance in high-fat diet (HFD)-induced diabetic mice. To test the direct effect of AmEVs on human epithelial cells, cultured Caco-2 cells were treated with these vesicles. AmEVs decreased the gut permeability of lipopolysaccharide-treated Caco-2 cells, whereas Escherichia coli-derived EVs had no significant effect. Interestingly, the expression of occludin was increased by AmEV treatment. Overall, these results imply that AmEVs may act as a functional moiety for controlling gut permeability and that the regulation of intestinal barrier integrity can improve metabolic functions in HFD-fed mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 May 28;110(22):9066-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219451110. Epub 2013 May 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23671105 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine treatment increases Akkermansia in the gut and improves high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in Apoe-/- mice.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Jan;268:117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.11.023. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 29202334
-
Navy bean supplemented high-fat diet improves intestinal health, epithelial barrier integrity and critical aspects of the obese inflammatory phenotype.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Aug;70:91-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 May 10. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31195365
-
Effects of gut microbiota-derived extracellular vesicles on obesity and diabetes and their potential modulation through diet.J Physiol Biochem. 2022 May;78(2):485-499. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00837-6. Epub 2021 Sep 2. J Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34472032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila: key player in metabolic and gastrointestinal disorders.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):8075-8083. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19024. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599433 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Artemisia asiatica ex on Akkermansia muciniphila dominance for modulation of Alzheimer's disease in mice.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 28;19(10):e0312670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312670. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39466764 Free PMC article.
-
The Gut-Brain Axis in Opioid Use Disorder: Exploring the Bidirectional Influence of Opioids and the Gut Microbiome-A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;14(10):1227. doi: 10.3390/life14101227. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akkermansia muciniphila for the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Animal Studies.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 11;16(20):3440. doi: 10.3390/nu16203440. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458436 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Pathobiont-Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles in the Oral-Gut Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 17;25(20):11141. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011141. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akkermansia beyond muciniphila - emergence of new species Akkermansia massiliensis sp. nov.Microbiome Res Rep. 2024 Jun 25;3(3):37. doi: 10.20517/mrr.2024.28. eCollection 2024. Microbiome Res Rep. 2024. PMID: 39421258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, Poggi M, Knauf C, Bastelica D et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007; 56: 1761–1772. - PubMed
-
- Osborn O, Olefsky JM. The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat Med 2012; 18: 363–374. - PubMed
-
- Collado MC, Isolauri E, Laitinen K, Salminen S. Distinct composition of gut microbiota during pregnancy in overweight and normal-weight women. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88: 894–899. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson CL, Onnerfalt J, Xu J, Molin G, Ahrne S, Thorngren-Jerneck K. The microbiota of the gut in preschool children with normal and excessive body weight. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2012; 20: 2257–2261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

