Combination of the low anticoagulant heparin CX-01 with chemotherapy for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 29467192
- PMCID: PMC5858478
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017013391
Combination of the low anticoagulant heparin CX-01 with chemotherapy for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
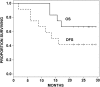
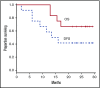
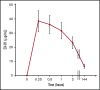
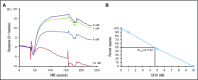
Relapses in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) are a result of quiescent leukemic stem cells (LSCs) in marrow stromal niches, where they resist chemotherapy. LSCs employ CXCL12/CXCR4 to home toward protective marrow niches. Heparin disrupts CXCL12-mediated sequestration of cells in the marrow. CX-01 is a low-anticoagulant heparin derivative. In this pilot study, we combined CX-01 with chemotherapy for the treatment of AML. Induction consisted of cytarabine and idarubicin (7 + 3) with CX-01. Twelve patients were enrolled (median age, 56 years; 3 women). Three, 5, and 4 patients had good-, intermediate-, and poor-risk disease, respectively. Day 14 bone marrows were available on 11 patients and were aplastic in all without detectable leukemia. Eleven patients (92%) had morphologic complete remission after 1 induction (CR1). Eight patients were alive at a median follow-up of 24 months (4 patients in CR1). Three patients received an allogeneic stem cell transplant in CR1. Median disease-free survival was 14.8 months. Median overall survival was not attained at the maximum follow-up time of 29.4 months. No CX-01-associated serious adverse events occurred. Median day to an untransfused platelet count of at least 20 × 109/L was 21. CX-01 is well tolerated when combined with intensive therapy for AML and appears associated with enhanced count recovery and treatment efficacy.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: T.P.K. is a stockholder in Cantex Pharmaceuticals. S.G.M. is employed by and is a stock holder in Cantex Pharmaceuticals. P.J.S. received research support from Cantex Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of dociparstat sodium (DSTAT), a CXCL12/CXCR4 inhibitor, with azacitidine for the treatment of hypomethylating agent refractory AML and MDS.Leuk Res. 2021 Nov;110:106713. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106713. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Leuk Res. 2021. PMID: 34619434 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Intensive chemotherapy for poor prognosis myelodysplasia (MDS) and secondary acute myeloid leukemia (sAML) following MDS of more than 6 months duration. A pilot study by the Leukemia Cooperative Group of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment in Cancer (EORTC-LCG).Leukemia. 1995 Nov;9(11):1805-11. Leukemia. 1995. PMID: 7475266 Clinical Trial.
-
Gemtuzumab-ozogamicin in combination with fludarabine, cytarabine, idarubicin (FLAI-GO) as induction therapy in CD33-positive AML patients younger than 65 years.Leuk Res. 2008 Dec;32(12):1800-8. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2008.05.011. Epub 2008 Jul 14. Leuk Res. 2008. PMID: 18621416 Clinical Trial.
-
Autologous transplantation of chemotherapy-purged PBSC collections from high-risk leukemia patients: a pilot study.Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999 Feb;23(3):235-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.bmt.1701576. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999. PMID: 10084254
-
Acute myelogenous leukemia subsequent to therapy for a different neoplasm: clinical features and response to therapy.Am J Hematol. 1977;3:209-18. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830030301. Am J Hematol. 1977. PMID: 341697 Review.
Cited by
-
Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia.Cells. 2019 Jan 17;8(1):66. doi: 10.3390/cells8010066. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30658474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Treatment Options for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in 2019.Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Feb 4;21(2):16. doi: 10.1007/s11912-019-0764-8. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30715623 Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of the Leukaemia Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 26;22(13):6888. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136888. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparan Sulfate Glycosaminoglycans: (Un)Expected Allies in Cancer Clinical Management.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 21;11(2):136. doi: 10.3390/biom11020136. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33494442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potential area of use for immune checkpoint inhibitors: Targeting bone marrow microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 20;14:1108200. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1108200. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36742324 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(1):9-29. - PubMed
-
- Estey EH. Acute myeloid leukemia: 2014 update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol. 2014;89(11):1063-1081. - PubMed
-
- Blau O. Bone marrow stromal cells in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Front Biosci. 2014;19(1):171-180. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Kollet O. The essential roles of the chemokine SDF-1 and its receptor CXCR4 in human stem cell homing and repopulation of transplanted immune-deficient NOD/SCID and NOD/SCID/B2m(null) mice. Leukemia. 2002;16(10):1992-2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

