Dietary Modulation of the Epigenome
- PMID: 29442595
- PMCID: PMC5966714
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00010.2017
Dietary Modulation of the Epigenome
Abstract
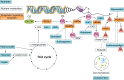
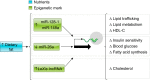
Epigenetics is the study of heritable mechanisms that can modify gene activity and phenotype without modifying the genetic code. The basis for the concept of epigenetics originated more than 2,000 yr ago as a theory to explain organismal development. However, the definition of epigenetics continues to evolve as we identify more of the components that make up the epigenome and dissect the complex manner by which they regulate and are regulated by cellular functions. A substantial and growing body of research shows that nutrition plays a significant role in regulating the epigenome. Here, we critically assess this diverse body of evidence elucidating the role of nutrition in modulating the epigenome and summarize the impact such changes have on molecular and physiological outcomes with regards to human health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The interaction between epigenetics, nutrition and the development of cancer.Nutrients. 2015 Jan 30;7(2):922-47. doi: 10.3390/nu7020922. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25647662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional modulation of the epigenome and its implication for future health.Proc Nutr Soc. 2019 Aug;78(3):305-312. doi: 10.1017/S0029665119000016. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Proc Nutr Soc. 2019. PMID: 30777143 Review.
-
Session 2: Personalised nutrition. Epigenomics: a basis for understanding individual differences?Proc Nutr Soc. 2008 Nov;67(4):390-4. doi: 10.1017/S0029665108008744. Proc Nutr Soc. 2008. PMID: 18847515 Review.
-
You are what you eat - How nutrition and metabolism shape the genome through epigenetics.Mol Metab. 2020 Aug;38:100987. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.100987. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32314738 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
What do studies of insect polyphenisms tell us about nutritionally-triggered epigenomic changes and their consequences?Nutrients. 2015 Mar 11;7(3):1787-97. doi: 10.3390/nu7031787. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25768950 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal vitamin D deficiency and developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD).J Endocrinol. 2019 Mar 1:JOE-18-0541.R2. doi: 10.1530/JOE-18-0541. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30909167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Oct 21;13(7):480-499. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab043. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34289049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research gaps and opportunities in precision nutrition: an NIH workshop report.Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Dec 19;116(6):1877-1900. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqac237. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36055772 Free PMC article.
-
Serum level of total histone 3, H3K4me3, and H3K27ac after non-emergent cardiac surgery suggests the persistence of smoldering inflammation at 3 months in an adult population.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Sep 6;14(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01331-6. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36068552 Free PMC article.
-
Intake of Natural Compounds and Circulating microRNA Expression Levels: Their Relationship Investigated in Healthy Subjects With Different Dietary Habits.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 14;11:619200. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.619200. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33519486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amarasekera M, Martino D, Ashley S, Harb H, Kesper D, Strickland D, Saffery R, Prescott SL. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiling identifies a folate-sensitive region of differential methylation upstream of ZFP57-imprinting regulator in humans. FASEB J 28: 4068–4076, 2014. doi:10.1096/fj.13-249029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson JG, Ramadori G, Ioris RM, Galiè M, Berglund ED, Coate KC, Fujikawa T, Pucciarelli S, Moreschini B, Amici A, Andreani C, Coppari R. Enhanced insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle and liver by physiological overexpression of SIRT6. Mol Metab 4: 846–856, 2015. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2015.09.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson KA, Huynh FK, Fisher-Wellman K, Stuart JD, Peterson BS, Douros JD, Wagner GR, Thompson JW, Madsen AS, Green MF, Sivley RM, Ilkayeva OR, Stevens RD, Backos DS, Capra JA, Olsen CA, Campbell JE, Muoio DM, Grimsrud PA, Hirschey MD. SIRT4 Is a Lysine Deacylase that Controls Leucine Metabolism and Insulin Secretion. Cell Metab 25: 838–855.e15, 2017. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2017.03.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

