Ethylene Signaling Modulates Cortical Microtubule Reassembly in Response to Salt Stress
- PMID: 29431630
- PMCID: PMC5841701
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.17.01124
Ethylene Signaling Modulates Cortical Microtubule Reassembly in Response to Salt Stress
Abstract
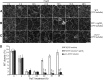
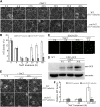
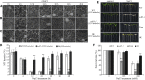
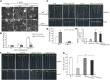
Regulation of cortical microtubule reorganization is essential for plant cell survival under high salinity conditions. In response to salt stress, microtubules undergo rapid depolymerization followed by reassembly to form a new microtubule network that promotes cell survival; however, the upstream regulatory mechanisms for this recovery response are largely unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that ethylene signaling facilitates salt stress-induced reassembly of cortical microtubules in Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). Microtubule depolymerization was not affected under salt stress following the suppression of ethylene signaling with Ag+ or in ethylene-insensitive mutants, whereas microtubule reassembly was significantly inhibited. ETHYLENE-INSENSITIVE3, a key transcription factor in the ethylene signaling pathway, was shown to play a central role in microtubule reassembly under salt stress. In addition, we performed functional characterization of the microtubule-stabilizing protein WAVE-DAMPENED2-LIKE5 (WDL5), which was found to promote ethylene-associated microtubule reassembly and plant salt stress tolerance. These findings indicate that ethylene signaling regulates microtubule reassembly by up-regulating WDL5 expression in response to salt stress, thereby implicating ethylene signaling in salt-stress tolerance in plants.
© 2018 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ethylene Regulates the Arabidopsis Microtubule-Associated Protein WAVE-DAMPENED2-LIKE5 in Etiolated Hypocotyl Elongation.Plant Physiol. 2015 Sep;169(1):325-37. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00609. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Plant Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26134166 Free PMC article.
-
A ROP2-RIC1 pathway fine-tunes microtubule reorganization for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Environ. 2017 Jul;40(7):1127-1142. doi: 10.1111/pce.12905. Epub 2017 Feb 24. Plant Cell Environ. 2017. PMID: 28070891
-
Submergence stress-induced hypocotyl elongation through ethylene signaling-mediated regulation of cortical microtubules in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2020 Jan 23;71(3):1067-1077. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz453. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 31638649
-
Ethylene signaling: simple ligand, complex regulation.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013 Oct;16(5):554-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24012247 Review.
-
Modulation of Ethylene and Ascorbic Acid on Reactive Oxygen Species Scavenging in Plant Salt Response.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Mar 18;10:319. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00319. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30936887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Plants Treated with a New Compound Natolen128, Enhancing Salt Stress Tolerance.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 14;10(5):978. doi: 10.3390/plants10050978. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068843 Free PMC article.
-
AtKATANIN1 Modulates Microtubule Depolymerization and Reorganization in Response to Salt Stress in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 24;21(1):138. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010138. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31878228 Free PMC article.
-
Ethylene: A Master Regulator of Plant-Microbe Interactions under Abiotic Stresses.Cells. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):31. doi: 10.3390/cells12010031. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional analyses of two soybean cultivars under salt stress.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Apr;47(4):2871-2888. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05398-3. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32227253
-
Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase-hydrolase30 negatively affects salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2019 Oct 15;70(19):5495-5506. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz311. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 31257449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G, Nourizadeh S, Ecker JR (1999) EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284: 2148–2152 - PubMed
-
- Asensi-Fabado MA, Cela J, Müller M, Arrom L, Chang C, Munné-Bosch S (2012) Enhanced oxidative stress in the ethylene-insensitive (ein3-1) mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 169: 360–368 - PubMed
-
- Ban Y, Kobayashi Y, Hara T, Hamada T, Hashimoto T, Takeda S, Hattori T (2013) α-tubulin is rapidly phosphorylated in response to hyperosmotic stress in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 54: 848–858 - PubMed
-
- Bashline L, Lei L, Li S, Gu Y (2014) Cell wall, cytoskeleton, and cell expansion in higher plants. Mol Plant 7: 586–600 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

