Time for a change: is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis still idiopathic and only fibrotic?
- PMID: 29413083
- PMCID: PMC5903445
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30007-9
Time for a change: is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis still idiopathic and only fibrotic?
Abstract
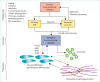
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive, irreversible, and typically fatal lung disease characterised by subpleural fibrosis, subepithelial fibroblast foci, and microscopic honeycombing. Although understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms continues to evolve, evidence indicates that distal airway and alveolar epithelial cells are central drivers of the disease. In this Viewpoint, we review the history of naming and classifications used to define the disease now referred to as IPF, in the context of understanding the clinical presentation, causes, and pathogenesis of the disease. We aim to generate discussion on whether, given the substantial progress made in understanding the clinical, genetic, cellular, and molecular mechanisms involved in the development of IPF, a change of name should be considered. To initiate this discussion, we offer new suggestions to update the name of this disease and new approaches to classify all forms of pulmonary fibrosis.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: idiopathic no more?Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Feb;6(2):84-85. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30022-5. Lancet Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29413084 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Wilms Tumor 1-Driven Fibroblast Activation and Subpleural Thickening in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2850. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032850. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The leading role of epithelial cells in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Signal. 2020 Feb;66:109482. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109482. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 31760172 Review.
-
Lung Fibroblasts, Aging, and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Dec;13 Suppl 5:S417-S421. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201605-341AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 28005427 Review.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evolving concepts.Mayo Clin Proc. 2014 Aug;89(8):1130-42. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.03.016. Epub 2014 May 24. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014. PMID: 24867394 Review.
-
Fibroblastic foci, covered with alveolar epithelia exhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, destroy alveolar septa by disrupting blood flow in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Lab Invest. 2017 Mar;97(3):232-242. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2016.135. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Lab Invest. 2017. PMID: 27941755
Cited by
-
Progress in Understanding and Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Annu Rev Med. 2019 Jan 27;70:211-224. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-041317-102715. Annu Rev Med. 2019. PMID: 30691371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Channels and Transporters of the Pulmonary Lamellar Body in Health and Disease.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):45. doi: 10.3390/cells11010045. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interstitial Lung Disease in Relatives of Patients with Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 May 15;201(10):1240-1248. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1571OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32011908 Free PMC article.
-
FibroVit-Vision transformer-based framework for detection and classification of pulmonary fibrosis from chest CT images.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 8;10:1282200. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1282200. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38020169 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of microRNA expression levels based on microarray analysis for classification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Oct;20(4):3096-3103. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9068. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32855677 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King TE, Jr, Pardo A, Selman M. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2011;378:1949–61. - PubMed
-
- Liebow AA. Definition and classification of interstitial pneumonias in human pathology. Prog Respir Res. 1975;8:1–31.
-
- Selman M, Pardo A. Revealing the pathogenic and aging-related mechanisms of the enigmatic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis an integral model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189:1161–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

