PD-L1 and IDO1 Are Expressed in Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
- PMID: 29372535
- PMCID: PMC6500591
- DOI: 10.1007/s12022-018-9514-y
PD-L1 and IDO1 Are Expressed in Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Abstract
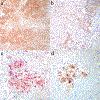
Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC) is an aggressive form of thyroid cancer that currently has limited effective treatment options. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have shown to be an effective treatment for a variety of carcinomas. In this study, we explore whether immune checkpoint pathways, such as programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), are activated in a cohort of patients with PDTC to determine whether ICIs may be an effective therapy for these patients. PDTC from 28 patients were stained for IDO1, PD-L1, and CD8 using immunohistochemistry. Staining was scored using an H-score, and PD-L1 and IDO1 expression was correlated with clinicopathologic characteristics. Positivity for PD-L1 and IDO1 was set at an H-score cutoff of five. Twenty-five percent (n = 7/28) of the PDTC were positive for PD-L1 expression. Twenty-nine percent (n = 2/7) of the PD-L1 positive PDTCs also co-expressed IDO1. The expression of PD-L1 in PDTC was significantly associated with tumor size and multifocality, with a non-significant trend towards associations with older age, extrathyroidal extension, presence of metastasis, higher stage, increased number of CD8+ T cells, and decreased disease-free and overall survival. PD-L1 expression occurs in a subset of PDTC, and is associated with a subset of clinical features of aggressive thyroid disease. Given the limited effective treatments for this patient population, consideration for ICIs as monotherapy or in combination with an IDO1 inhibitor should be explored as a novel treatment modality for patients with PDTC.
Keywords: IDO1; Immune checkpoint; Immuno-oncology; Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1; PD-L1; PD1; Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma; Programmed cell death ligand 1.
Figures
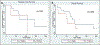
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of PD-L1 and IDO1 in association with the immune microenvironment in resected lung adenocarcinomas.Mod Pathol. 2019 Apr;32(4):511-523. doi: 10.1038/s41379-018-0160-1. Epub 2018 Oct 26. Mod Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30367104
-
Programmed death ligand 1/indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte status in renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid changes and rhabdoid features.Hum Pathol. 2020 Jul;101:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Hum Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32360490
-
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 and programmed cell death-ligand 1 co-expression correlates with aggressive features in lung adenocarcinoma.Eur J Cancer. 2018 Sep;101:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.06.020. Epub 2018 Jul 13. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30014971
-
From biomarkers to therapeutic targets: the promise of PD-L1 in thyroid autoimmunity and cancer.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(3):1310-1325. doi: 10.7150/thno.50333. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy for endocrine tumours: a clinician's perspective.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;31(4):e230296. doi: 10.1530/ERC-23-0296. Print 2024 Apr 1. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38235757 Review.
Cited by
-
Systemic treatments for radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 15;15:1346476. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1346476. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39473507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAK4 Is Involved in the Stabilization of PD-L1 and the Resistance to Doxorubicin in Osteosarcoma and Predicts the Survival of Diagnosed Patients.Cells. 2024 Aug 28;13(17):1444. doi: 10.3390/cells13171444. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39273017 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring markers of immunoresponsiveness in papillary thyroid carcinoma and future treatment strategies.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jul 29;12(7):e008505. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008505. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39074963 Free PMC article.
-
Pembrolizumab plus either epacadostat or placebo for cisplatin-ineligible urothelial carcinoma: results from the ECHO-307/KEYNOTE-672 study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;23(Suppl 1):1252. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10727-3. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39054491 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Epacadostat plus pembrolizumab versus placebo plus pembrolizumab for advanced urothelial carcinoma: results from the randomized phase III ECHO-303/KEYNOTE-698 study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;23(Suppl 1):1256. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11213-6. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39054485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Volante M, Collini P, Nikiforov YE, et al. (2007) Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma: the Turin proposal for the use of uniform diagnostic criteria and an algorithmic diagnostic approach. Am J Surg Pathol 31:1256–1264 - PubMed
-
- Kakudo K, Bai Y, Katayama S, et al. (2009) Classification of follicular cell tumors of the thyroid gland: Analysis involving Japanese patients from one institute. Pathol Int 59:359–367 - PubMed
-
- Sanders EM, LiVolsi VA, Brierley J, et al. (2007) An evidence-based review of poorly differentiated thyroid cancer. World J Surg 31:934–945 - PubMed
-
- Lai HW, Lee CH, Chen JY, et al. (2006) Insular Thyroid Carcinoma: Collective Analysis of Clinicohistologic Prognostic Factors and Treatment Effect with Radioiodine or Radiation Therapy. J Am Coll Surg 203:715–722 - PubMed
-
- Patel KN, Shaha AR (2014) Poorly differentiated thyroid cancer. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 22:121–6 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

