ATF3 represses PINK1 gene transcription in lung epithelial cells to control mitochondrial homeostasis
- PMID: 29363258
- PMCID: PMC5847866
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12720
ATF3 represses PINK1 gene transcription in lung epithelial cells to control mitochondrial homeostasis
Abstract
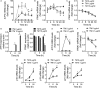
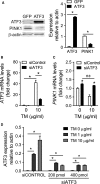
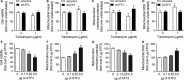
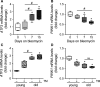
PINK1 (PTEN-induced putative kinase 1) is a key regulator of mitochondrial homeostasis that is relatively depleted in aging lungs and in lung epithelial cells from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a disease linked with aging. Impaired PINK1 expression and accumulation of damaged mitochondria in lung epithelial cells from fibrotic lungs were associated with the presence of ER stress. Here, we show that ATF3 (activating transcription factor 3), a member of the integrated stress response (ISR), negatively regulates transcription of the PINK1 gene. An ATF3 binding site within the human PINK1 promoter is located in the first 150 bp upstream of the transcription start site. Induction of ER stress or overexpression of ATF3 inhibited the activity of the PINK1 promoter. Importantly, overexpression of ATF3 causes accumulation of depolarized mitochondria, increased production of mitochondrial ROS, and loss of cell viability. Furthermore, conditional deletion of ATF3 in type II lung epithelial cells protects mice from bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Finally, we observed that ATF3 expression increases in the lung with age and, specially, in lung epithelial cells from IPF lungs. These data provide a unique link between ATF3 and PINK1 expression suggesting that persistent stress, driven by ATF3, can dysregulate mitochondrial homeostasis by repression of PINK1 mRNA synthesis.
Keywords: ER stress; PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; activating transcription factor 3; aging; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; mitochondrial dysfunction.
© 2018 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Citrus alkaline extracts prevent endoplasmic reticulum stress in type II alveolar epithelial cells to ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis via the ATF3/PINK1 pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 Aug;89:153599. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153599. Epub 2021 May 21. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34260993
-
Mitochondrial 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase mitigates alveolar epithelial cell PINK1 deficiency, mitochondrial DNA damage, apoptosis, and lung fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):L1084-L1096. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00069.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32209025 Free PMC article.
-
PINK1 deficiency impairs mitochondrial homeostasis and promotes lung fibrosis.J Clin Invest. 2015 Feb;125(2):521-38. doi: 10.1172/JCI74942. Epub 2014 Dec 22. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25562319 Free PMC article.
-
PINK1-PARK2-mediated mitophagy in COPD and IPF pathogeneses.Inflamm Regen. 2018 Oct 24;38:18. doi: 10.1186/s41232-018-0077-6. eCollection 2018. Inflamm Regen. 2018. PMID: 30386443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lost after translation: insights from pulmonary surfactant for understanding the role of alveolar epithelial dysfunction and cellular quality control in fibrotic lung disease.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):L507-25. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00139.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26186947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C/EBP homologous protein promotes Sonic Hedgehog secretion from type II alveolar epithelial cells and activates Hedgehog signaling pathway of fibroblast in pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Res. 2022 Apr 8;23(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02012-x. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35395850 Free PMC article.
-
CYB5R3 in type II alveolar epithelial cells protects against lung fibrosis by suppressing TGF-β1 signaling.JCI Insight. 2023 Mar 8;8(5):e161487. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.161487. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 36749633 Free PMC article.
-
MOTS-c repairs myocardial damage by inhibiting the CCN1/ERK1/2/EGR1 pathway in diabetic rats.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 4;9:1060684. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1060684. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36687680 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Adv Respir Med. 2023 Jan 31;91(1):26-48. doi: 10.3390/arm91010005. Adv Respir Med. 2023. PMID: 36825939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causes of Pulmonary Fibrosis in the Elderly.Med Sci (Basel). 2018 Jul 24;6(3):58. doi: 10.3390/medsci6030058. Med Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30042329 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armanios, M. Y. , Chen, J. J. , Cogan, J. D. , Alder, J. K. , Ingersoll, R. G. , Markin, C. , … Loyd, J. E. (2007). Telomerase mutations in families with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The New England Journal of Medicine, 356, 1317–1326. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa066157 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bueno, M. , Lai, Y. C. , Romero, Y. , Brands, J. , St Croix, C. M. , Kamga, C. , … Mora, A. L. (2015). PINK1 deficiency impairs mitochondrial homeostasis and promotes lung fibrosis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 125, 521–538. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI74942 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chambers, R. C. , Leoni, P. , Kaminski, N. , Laurent, G. J. , & Heller, R. A. (2003). Global expression profiling of fibroblast responses to transforming growth factor‐β1 reveals the induction of inhibitor of differentiation‐1 and provides evidence of smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. American Journal of Pathology, 162, 533–546. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63847-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, B. P. , Wolfgang, C. D. , & Hai, T. (1996). Analysis of ATF3, a transcription factor induced by physiological stresses and modulated by gadd153/Chop10. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 16, 1157–1168. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.16.3.1157 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duan, X. , Tong, J. , Xu, Q. , Wu, Y. , Cai, F. , Li, T. , & Song, W. (2014). Upregulation of human PINK1 gene expression by NFkappaB signalling. Molecular Brain, 7, 57 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-014-0057-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

