The role of Nrf2 signaling in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 29323772
- PMCID: PMC6221096
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14379
The role of Nrf2 signaling in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
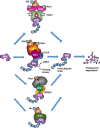
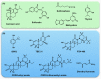
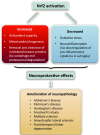
The transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor-erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2) functions at the interface of cellular redox and intermediary metabolism. Nrf2 target genes encode antioxidant enzymes, and proteins involved in xenobiotic detoxification, repair and removal of damaged proteins and organelles, inflammation, and mitochondrial bioenergetics. The function of Nrf2 is altered in many neurodegenerative disorders, such as Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Friedreich's ataxia. Nrf2 activation mitigates multiple pathogenic processes involved in these neurodegenerative disorders through upregulation of antioxidant defenses, inhibition of inflammation, improvement of mitochondrial function, and maintenance of protein homeostasis. Small molecule pharmacological activators of Nrf2 have shown protective effects in numerous animal models of neurodegenerative diseases, and in cultures of human cells expressing mutant proteins. Targeting Nrf2 signaling may provide a therapeutic option to delay onset, slow progression, and ameliorate symptoms of neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Nrf2 activator; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; neuroprotection; oxidative stress.
© 2018 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nrf2 activation in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a focus on its role in mitochondrial bioenergetics and function.Biol Chem. 2016 May;397(5):383-400. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2015-0295. Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26812787 Review.
-
Nrf2--a therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):253-267. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.07.147. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26281945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NRF2 and NF-қB interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches.Redox Biol. 2019 Feb;21:101059. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.11.017. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30576920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of the Nrf2/ARE Pathway and Its Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 4;22(17):9592. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179592. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nrf2-ARE pathway: a valuable therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2012 Dec;7(3):218-29. doi: 10.2174/157488912803252023. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22742419 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nrf2 and STAT3 Alleviates Ferroptosis-Mediated IIR-ALI by Regulating SLC7A11.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 18;2020:5146982. doi: 10.1155/2020/5146982. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33014271 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway in airway innate immunity.World J Biol Chem. 2020 Sep 27;11(2):30-51. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v11.i2.30. World J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33024516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neuroprotective effects of icariin on ageing, various neurological, neuropsychiatric disorders, and brain injury induced by radiation exposure.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Feb 14;14(3):1562-1588. doi: 10.18632/aging.203893. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35165207 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 Induction Re-establishes a Proper Neuronal Differentiation Program in Friedreich's Ataxia Neural Stem Cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Jul 31;13:356. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00356. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31417369 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Potential, Gastrointestinal Digestion, Absorption, and Bioavailability of Algae-Derived Compounds with Neuroprotective Activity: A Comprehensive Review.Mar Drugs. 2022 May 28;20(6):362. doi: 10.3390/md20060362. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736165 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hayes JD & Dinkova‐Kostova AT (2014) The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 39, 199–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

