Skeletal Muscle-Specific Deletion of MKP-1 Reveals a p38 MAPK/JNK/Akt Signaling Node That Regulates Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 29317435
- PMCID: PMC5860856
- DOI: 10.2337/db17-0826
Skeletal Muscle-Specific Deletion of MKP-1 Reveals a p38 MAPK/JNK/Akt Signaling Node That Regulates Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance
Abstract
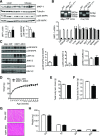
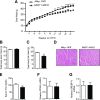
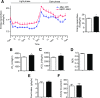
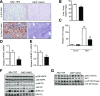
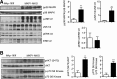
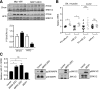
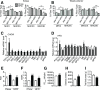
Stress responses promote obesity and insulin resistance, in part, by activating the stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), p38 MAPK, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK). Stress also induces expression of MAPK phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), which inactivates both JNK and p38 MAPK. However, the equilibrium between JNK/p38 MAPK and MKP-1 signaling in the development of obesity and insulin resistance is unclear. Skeletal muscle is a major tissue involved in energy expenditure and glucose metabolism. In skeletal muscle, MKP-1 is upregulated in high-fat diet-fed mice and in skeletal muscle of obese humans. Mice lacking skeletal muscle expression of MKP-1 (MKP1-MKO) showed increased skeletal muscle p38 MAPK and JNK activities and were resistant to the development of diet-induced obesity. MKP1-MKO mice exhibited increased whole-body energy expenditure that was associated with elevated levels of myofiber-associated mitochondrial oxygen consumption. miR-21, a negative regulator of PTEN expression, was upregulated in skeletal muscle of MKP1-MKO mice, resulting in increased Akt activity consistent with enhanced insulin sensitivity. Our results demonstrate that skeletal muscle MKP-1 represents a critical signaling node through which inactivation of the p38 MAPK/JNK module promotes obesity and insulin resistance.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mice lacking MAP kinase phosphatase-1 have enhanced MAP kinase activity and resistance to diet-induced obesity.Cell Metab. 2006 Jul;4(1):61-73. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.05.010. Cell Metab. 2006. PMID: 16814733
-
Metabolic Impact of MKP-2 Upregulation in Obesity Promotes Insulin Resistance and Fatty Liver Disease.Nutrients. 2022 Jun 15;14(12):2475. doi: 10.3390/nu14122475. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35745205 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 selectively regulates glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;35(1):26-40. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00503-14. Epub 2014 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25312648 Free PMC article.
-
p38 MAPK in Glucose Metabolism of Skeletal Muscle: Beneficial or Harmful?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6480. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186480. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protecting the stress response, guarding the MKP-1 mRNA.Cell Cycle. 2008 Sep 1;7(17):2640-2. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.17.6534. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18728392 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An allosteric site on MKP5 reveals a strategy for small-molecule inhibition.Sci Signal. 2020 Aug 25;13(646):eaba3043. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aba3043. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32843541 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of PTP1B Promotes M2 Polarization via MicroRNA-26a/MKP1 Signaling Pathway in Murine Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 14;10:1930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01930. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31474996 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-Specificity Phosphatases in Immunity and Infection: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 2;20(11):2710. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112710. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31159473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic changes in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis: state of the art review.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1250884. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1250884. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38482018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling pathways in obesity: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 28;7(1):298. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01149-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36031641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

