Mechanosensing and fibrosis
- PMID: 29293092
- PMCID: PMC5749510
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI93561
Mechanosensing and fibrosis
Abstract
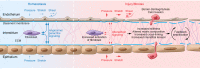
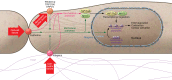
Tissue injury disrupts the mechanical homeostasis that underlies normal tissue architecture and function. The failure to resolve injury and restore homeostasis gives rise to progressive fibrosis that is accompanied by persistent alterations in the mechanical environment as a consequence of pathological matrix deposition and stiffening. This Review focuses on our rapidly growing understanding of the molecular mechanisms linking the altered mechanical environment in injury, repair, and fibrosis to cellular activation. In particular, our focus is on the mechanisms by which cells transduce mechanical signals, leading to transcriptional and epigenetic responses that underlie both transient and persistent alterations in cell state that contribute to fibrosis. Translation of these mechanobiological insights may enable new approaches to promote tissue repair and arrest or reverse fibrotic tissue remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanotransduction in fibrosis: Mechanisms and treatment targets.Curr Top Membr. 2021;87:279-314. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Curr Top Membr. 2021. PMID: 34696888 Review.
-
Matrix Mechanics as Regulatory Factors and Therapeutic Targets in Hepatic Fibrosis.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Sep 7;15(12):2509-2521. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.37500. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31754325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The matrix environmental and cell mechanical properties regulate cell migration and contribute to the invasive phenotype of cancer cells.Rep Prog Phys. 2019 Jun;82(6):064602. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ab1628. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Rep Prog Phys. 2019. PMID: 30947151 Review.
-
Mechanosensing in liver regeneration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Nov;71:153-167. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.07.041. Epub 2017 Jul 30. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28768152 Review.
-
Regulation of tissue fibrosis by the biomechanical environment.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:101979. doi: 10.1155/2013/101979. Epub 2013 May 28. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23781495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acute contact with profibrotic macrophages mechanically activates fibroblasts via αvβ3 integrin-mediated engagement of Piezo1.Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 25;10(43):eadp4726. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp4726. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39441936 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanoregulation of YAP and TAZ in Cellular Homeostasis and Disease Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 24;9:673599. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.673599. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34109179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechano-Signaling Aspects of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2021 Sep 3;12(21):6411-6421. doi: 10.7150/jca.60102. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34659531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implant Fibrosis and the Underappreciated Role of Myofibroblasts in the Foreign Body Reaction.Cells. 2021 Jul 15;10(7):1794. doi: 10.3390/cells10071794. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From ARDS to pulmonary fibrosis: the next phase of the COVID-19 pandemic?Transl Res. 2022 Mar;241:13-24. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2021.09.001. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 34547499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

