Opening of the human epithelial calcium channel TRPV6
- PMID: 29258289
- PMCID: PMC5854407
- DOI: 10.1038/nature25182
Opening of the human epithelial calcium channel TRPV6
Abstract
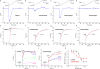
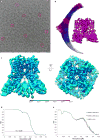
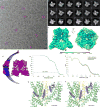
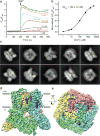
Calcium-selective transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily member 6 (TRPV6) channels play a critical role in calcium uptake in epithelial tissues. Altered TRPV6 expression is associated with a variety of human diseases, including cancers. TRPV6 channels are constitutively active and their open probability depends on the lipidic composition of the membrane in which they reside; it increases substantially in the presence of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Crystal structures of detergent-solubilized rat TRPV6 in the closed state have previously been solved. Corroborating electrophysiological results, these structures demonstrated that the Ca2+ selectivity of TRPV6 arises from a ring of aspartate side chains in the selectivity filter that binds Ca2+ tightly. However, how TRPV6 channels open and close their pores for ion permeation has remained unclear. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of human TRPV6 in the open and closed states. The channel selectivity filter adopts similar conformations in both states, consistent with its explicit role in ion permeation. The iris-like channel opening is accompanied by an α-to-π-helical transition in the pore-lining transmembrane helix S6 at an alanine hinge just below the selectivity filter. As a result of this transition, the S6 helices bend and rotate, exposing different residues to the ion channel pore in the open and closed states. This gating mechanism, which defines the constitutive activity of TRPV6, is, to our knowledge, unique among tetrameric ion channels and provides structural insights for understanding their diverse roles in physiology and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures


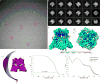



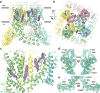
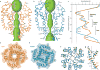
Similar articles
-
Structure and function of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6.J Physiol. 2021 May;599(10):2673-2697. doi: 10.1113/JP279024. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32073143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determining the Crystal Structure of TRPV6.In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 14. In: Kozak JA, Putney JW Jr, editors. Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2018. Chapter 14. PMID: 30299652 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Mechanism of calmodulin inactivation of the calcium-selective TRP channel TRPV6.Sci Adv. 2018 Aug 15;4(8):eaau6088. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau6088. eCollection 2018 Aug. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 30116787 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved gating element in TRPV6 channels.Cell Calcium. 2017 May;63:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Cell Calcium. 2017. PMID: 28029385
-
Ion Permeation Mechanism in Epithelial Calcium Channel TRVP6.Sci Rep. 2018 Apr 9;8(1):5715. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23972-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29632318 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Single-particle cryo-EM structure of a voltage-activated potassium channel in lipid nanodiscs.Elife. 2018 Aug 15;7:e37558. doi: 10.7554/eLife.37558. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30109985 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and Reconstitution of TRPV1 for Spectroscopic Analysis.J Vis Exp. 2018 Jul 3;(137):57796. doi: 10.3791/57796. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30035769 Free PMC article.
-
Purification and cryo-EM structure determination of Arabidopsis thaliana GLR3.4.STAR Protoc. 2021 Oct 1;2(4):100855. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100855. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34647037 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the gating mechanisms of TRPV channels.Cell Calcium. 2020 May;87:102168. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2020.102168. Epub 2020 Jan 24. Cell Calcium. 2020. PMID: 32004816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thresholding of cryo-EM density maps by false discovery rate control.IUCrJ. 2019 Jan 1;6(Pt 1):18-33. doi: 10.1107/S2052252518014434. eCollection 2019 Jan 1. IUCrJ. 2019. PMID: 30713700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng JB, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a channel-like transporter mediating intestinal calcium absorption. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:22739–22746. - PubMed
-
- Yue L, Peng JB, Hediger MA, Clapham DE. CaT1 manifests the pore properties of the calcium-release-activated calcium channel. Nature. 2001;410:705–709. - PubMed
-
- Owsianik G, Talavera K, Voets T, Nilius B. Permeation and selectivity of TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:685–717. - PubMed
-
- Woudenberg-Vrenken TE, et al. Functional TRPV6 channels are crucial for transepithelial Ca2+ absorption. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012;303:G879–885. - PubMed
-
- Fecher-Trost C, Weissgerber P, Wissenbach U. TRPV6 channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:359–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

