Indole-3-propionic acid suppresses indoxyl sulfate-induced expression of fibrotic and inflammatory genes in proximal tubular cells
- PMID: 29238104
- PMCID: PMC5719207
- DOI: 10.18999/nagjms.79.4.477
Indole-3-propionic acid suppresses indoxyl sulfate-induced expression of fibrotic and inflammatory genes in proximal tubular cells
Abstract
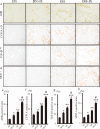
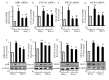
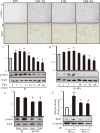
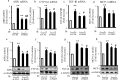
Indoxyl sulfate (IS) induces fibrosis and inflammation in kidneys via oxidative stress through the induction of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1). Furthermore, IS is a potent endogenous agonist for aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), which regulates the transcription of genes such as cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A1. Indole-3-propionic acid (IPA) is an antioxidant and has been reported to be neuroprotective. We determined whether IPA suppresses IS-induced expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 in proximal tubular cells. The effects of IS on the expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 were studied using normotensive rats and hypertensive rats. The effects of IPA on IS-induced expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 were studied using proximal tubular cells (HK-2). Furthermore, the effects of IPA on IS-induced expression and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) were studied in HK-2 cells. Administration of IS induced the expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 in the tubular cells of rat kidneys. IPA significantly suppressed IS-induced mRNA and protein expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 in HK-2 cells. IPA suppressed the IS-induced expression and phosphorylation of Stat3 in HK-2 cells. Furthermore, knockdown of Stat3 inhibited the IS-induced mRNA and protein expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 in HK-2 cells. In conclusion, IPA suppressed the IS-induced expression of AHR, CYP1A1, TGF-β1, and MCP-1 through suppression of Stat3 in proximal tubular cells. Thus, IPA suppresses IS-induced expression of fibrotic and inflammatory genes in proximal tubular cells.
Keywords: TGF-β1; aryl hydrocarbon receptor; indole-3-propionic acid; indoxyl sulfate; proximal tubular cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Indoxyl sulfate downregulates expression of Mas receptor via OAT3/AhR/Stat3 pathway in proximal tubular cells.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e91517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091517. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24614509 Free PMC article.
-
Indoxyl sulfate-induced activation of (pro)renin receptor is involved in expression of TGF-β1 and α-smooth muscle actin in proximal tubular cells.Endocrinology. 2014 May;155(5):1899-907. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1937. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24601883
-
Indoxyl sulfate enhances p53-TGF-β1-Smad3 pathway in proximal tubular cells.Am J Nephrol. 2013;37(2):97-103. doi: 10.1159/000346420. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Am J Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23363842
-
Indoxyl Sulfate, a Tubular Toxin, Contributes to the Development of Chronic Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Oct 29;12(11):684. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110684. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33138205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and its endogenous agonist - indoxyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2017 Jul 30;71(0):624-632. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.3843. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2017. PMID: 28791957 Review.
Cited by
-
The Neuroprotective Role of Indole-3-Propionic Acid in Migraine Pathophysiology.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 30;60(9):1417. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091417. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336458 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Fibrogenesis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Exploring the Potential Role of Gut Microbiota Metabolites as Modulators.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;17(4):490. doi: 10.3390/ph17040490. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolites Associated With Uremic Symptoms in Patients With CKD: Findings From the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2024 Jul;84(1):49-61.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.11.013. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2024. PMID: 38266973
-
The AKI-to-CKD Transition: The Role of Uremic Toxins.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 10;24(22):16152. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216152. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indole Propionic Acid Increases T Regulatory Cells and Decreases T Helper 17 Cells and Blood Pressure in Mice with Salt-Sensitive Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 24;24(11):9192. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119192. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niwa T, Ise M. Indoxyl sulfate, a circulating uremic toxin, stimulates the progression of glomerular sclerosis. J Lab Clin Med, 1994; 124: 96-104. - PubMed
-
- Niwa T, Ise M, Miyazaki T. Progression of glomerular sclerosis in experimental uremic rats by administration of indole, a precursor of indoxyl sulfate. Am J Nephrol, 1994; 14: 207-212. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T, Ise M, Seo H, Niwa T. Indoxyl sulfate increases the gene expressions of TGF-beta1, TIMP-1 and pro-alpha 1(I) collagen in uremic rat kidneys. Kidney Int, 1997; S62: S15-22. - PubMed
-
- Niwa T, Indoxyl sulfate is a nephro-vascular toxin. J Ren Nutr, 2010; 20(Suppl 1): S2-S6. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu H, Bolati D, Adijiang A, Enomoto A, Nishijima F, Dateki M, et al. Senescence and dysfunction of proximal tubular cells are associated with activated p53 expression by indoxyl sulfate. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2010; 299: C1110-C1117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
