Origin and differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells after vaccination
- PMID: 29236685
- PMCID: PMC6037316
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24633
Origin and differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells after vaccination
Abstract
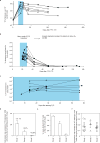
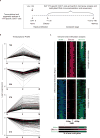
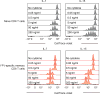
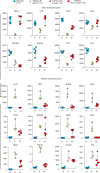
The differentiation of human memory CD8 T cells is not well understood. Here we address this issue using the live yellow fever virus (YFV) vaccine, which induces long-term immunity in humans. We used in vivo deuterium labelling to mark CD8 T cells that proliferated in response to the virus and then assessed cellular turnover and longevity by quantifying deuterium dilution kinetics in YFV-specific CD8 T cells using mass spectrometry. This longitudinal analysis showed that the memory pool originates from CD8 T cells that divided extensively during the first two weeks after infection and is maintained by quiescent cells that divide less than once every year (doubling time of over 450 days). Although these long-lived YFV-specific memory CD8 T cells did not express effector molecules, their epigenetic landscape resembled that of effector CD8 T cells. This open chromatin profile at effector genes was maintained in memory CD8 T cells isolated even a decade after vaccination, indicating that these cells retain an epigenetic fingerprint of their effector history and remain poised to respond rapidly upon re-exposure to the pathogen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


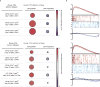
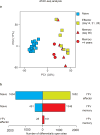

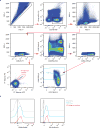
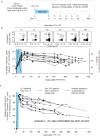


Comment in
-
The origins of memory T cells.Nature. 2017 Dec 21;552(7685):337-339. doi: 10.1038/d41586-017-08280-8. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29293221 No abstract available.
-
Heavy Water Shedding Light on Antigen-Specific T Cell Responses.Trends Immunol. 2018 Mar;39(3):170-172. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Trends Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29396015
Similar articles
-
Temporal dynamics of the primary human T cell response to yellow fever virus 17D as it matures from an effector- to a memory-type response.J Immunol. 2013 Mar 1;190(5):2150-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202234. Epub 2013 Jan 21. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23338234
-
The yellow fever virus vaccine induces a broad and polyfunctional human memory CD8+ T cell response.J Immunol. 2009 Dec 15;183(12):7919-30. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803903. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19933869 Free PMC article.
-
Long-lasting stem cell-like memory CD8+ T cells with a naïve-like profile upon yellow fever vaccination.Sci Transl Med. 2015 Apr 8;7(282):282ra48. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa3700. Sci Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25855494
-
Insights into human CD8(+) T-cell memory using the yellow fever and smallpox vaccines.Immunol Cell Biol. 2011 Mar;89(3):340-5. doi: 10.1038/icb.2010.155. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21301482 Review.
-
Generating long-lived CD8(+) T-cell memory: Insights from epigenetic programs.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Jul;46(7):1548-62. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545550. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27230488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What are the roles of antibodies versus a durable, high quality T-cell response in protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2?Vaccine X. 2020 Dec 11;6:100076. doi: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2020.100076. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Vaccine X. 2020. PMID: 32875286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The profile and prognostic significance of bone marrow T-cell differentiation subsets in adult AML at diagnosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1418792. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1418792. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39100667 Free PMC article.
-
Robust induction of B cell and T cell responses by a third dose of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.Cell Discov. 2022 Feb 1;8(1):10. doi: 10.1038/s41421-022-00373-7. Cell Discov. 2022. PMID: 35102140 Free PMC article.
-
Proliferating Transitory T Cells with an Effector-like Transcriptional Signature Emerge from PD-1+ Stem-like CD8+ T Cells during Chronic Infection.Immunity. 2019 Dec 17;51(6):1043-1058.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.002. Epub 2019 Dec 3. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31810882 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Level Computational Modeling of Anti-Cancer Dendritic Cell Vaccination Utilized to Select Molecular Targets for Therapy Optimization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 2;9:746359. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.746359. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35186943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Lau LL, Jamieson BD, Somasundaram T, Ahmed R. Cytotoxic T-cell memory without antigen. Nature. 1994;369:648–652. - PubMed
-
- Nanan R, Rauch A, Kämpgen E, Niewiesk S, Kreth HW. A novel sensitive approach for frequency analysis of measles virus-specific memory T-lymphocytes in healthy adults with a childhood history of natural measles. J. Gen. Virol. 2000;81:1313–1319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

