Application of Generative Autoencoder in De Novo Molecular Design
- PMID: 29235269
- PMCID: PMC5836887
- DOI: 10.1002/minf.201700123
Application of Generative Autoencoder in De Novo Molecular Design
Abstract
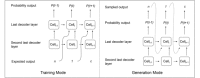
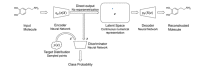
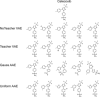
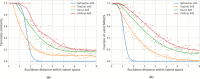
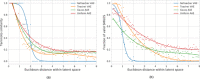
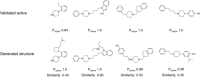
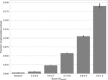
A major challenge in computational chemistry is the generation of novel molecular structures with desirable pharmacological and physiochemical properties. In this work, we investigate the potential use of autoencoder, a deep learning methodology, for de novo molecular design. Various generative autoencoders were used to map molecule structures into a continuous latent space and vice versa and their performance as structure generator was assessed. Our results show that the latent space preserves chemical similarity principle and thus can be used for the generation of analogue structures. Furthermore, the latent space created by autoencoders were searched systematically to generate novel compounds with predicted activity against dopamine receptor type 2 and compounds similar to known active compounds not included in the trainings set were identified.
Keywords: Autoencoder; chemoinformatics; de novo molecular design; deep learning; inverse QSAR.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
De Novo Molecular Design by Combining Deep Autoencoder Recurrent Neural Networks with Generative Topographic Mapping.J Chem Inf Model. 2019 Mar 25;59(3):1182-1196. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.8b00751. Epub 2019 Mar 5. J Chem Inf Model. 2019. PMID: 30785751
-
Deep Generative Models for Molecular Science.Mol Inform. 2018 Jan;37(1-2). doi: 10.1002/minf.201700133. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Mol Inform. 2018. PMID: 29405647 Review.
-
Improving Chemical Autoencoder Latent Space and Molecular De Novo Generation Diversity with Heteroencoders.Biomolecules. 2018 Oct 30;8(4):131. doi: 10.3390/biom8040131. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30380783 Free PMC article.
-
De novo design with deep generative models based on 3D similarity scoring.Bioorg Med Chem. 2021 Aug 15;44:116308. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116308. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Bioorg Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34280849
-
Generative Deep Learning for Targeted Compound Design.J Chem Inf Model. 2021 Nov 22;61(11):5343-5361. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.0c01496. Epub 2021 Oct 26. J Chem Inf Model. 2021. PMID: 34699719 Review.
Cited by
-
The Advent of Generative Chemistry.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Jul 14;11(8):1496-1505. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00088. eCollection 2020 Aug 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32832015 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating QSAR modelling and deep learning in drug discovery: the emergence of deep QSAR.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Feb;23(2):141-155. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00832-0. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38066301 Review.
-
Who Is Metabolizing What? Discovering Novel Biomolecules in the Microbiome and the Organisms Who Make Them.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jul 31;10:388. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00388. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32850487 Free PMC article.
-
Retro Drug Design: From Target Properties to Molecular Structures.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 12:2021.05.11.442656. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.11.442656. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2022 Jun 13;62(11):2659-2669. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00123 PMID: 34013260 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
MOLER: Incorporate Molecule-Level Reward to Enhance Deep Generative Model for Molecule Optimization.IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2022 Nov;34(11):5459-5471. doi: 10.1109/tkde.2021.3052150. Epub 2021 Jan 21. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2022. PMID: 36590707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma J., Sheridan R. P., Liaw A., Dahl G. E., Svetnik V., J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 263–274. - PubMed
-
- Segler M. H. S., Kogej T., Tyrchan C., Waller M. P., ArXiv:1701.01329 Phys. Stat 2017.
-
- Jaques N., Gu S., Bahdanau D., Lobato J. M. H., Turner R. E., Eck D., ArXiv:1611.02796 Cs 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

