Systematic analysis of ribophagy in human cells reveals bystander flux during selective autophagy
- PMID: 29230017
- PMCID: PMC5786475
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-017-0007-x
Systematic analysis of ribophagy in human cells reveals bystander flux during selective autophagy
Abstract
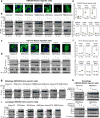
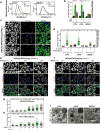
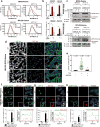
Ribosomes are abundant cellular machines 1,2 that are regulated by assembly, supernumerary subunit turnover and nascent chain quality control mechanisms 1-5 . Moreover, nitrogen starvation in yeast has been reported to promote selective ribosome delivery to the vacuole in an autophagy conjugation system dependent manner, a process called 'ribophagy' 6,7 . However, whether ribophagy in mammals is selective or regulated is unclear. Using Ribo-Keima flux reporters, we find that starvation or mTOR inhibition promotes VPS34-dependent ribophagic flux, which, unlike yeast, is largely independent of ATG8 conjugation and occurs concomitantly with other cytosolic protein autophagic flux reporters 8,9 . Ribophagic flux was not induced upon inhibition of translational elongation or nascent chain uncoupling, but was induced in a comparatively selective manner under proteotoxic stress induced by arsenite 10 or chromosome mis-segregation 11 , dependent upon VPS34 and ATG8 conjugation. Unexpectedly, agents typically used to induce selective autophagy also promoted increased ribosome and cytosolic protein reporter flux, suggesting significant bulk or 'bystander' autophagy during what is often considered selective autophagy 12,13 . These results emphasize the importance of monitoring non-specific cargo flux when assessing selective autophagy pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mature ribosomes are selectively degraded upon starvation by an autophagy pathway requiring the Ubp3p/Bre5p ubiquitin protease.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 May;10(5):602-10. doi: 10.1038/ncb1723. Epub 2008 Apr 6. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18391941
-
γ-Glutamyl kinase is involved in selective autophagy of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.FEBS Lett. 2016 Sep;590(17):2906-14. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12318. Epub 2016 Aug 4. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27442630
-
The Ins and Outs of Autophagic Ribosome Turnover.Cells. 2019 Dec 10;8(12):1603. doi: 10.3390/cells8121603. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31835634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GST-BHMT assay reveals a distinct mechanism underlying proteasome inhibition-induced macroautophagy in mammalian cells.Autophagy. 2015;11(5):812-32. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1034402. Autophagy. 2015. PMID: 25984893 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome Abundance Control Via the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and Autophagy.J Mol Biol. 2020 Jan 3;432(1):170-184. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 11. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31195016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibiting TrxR suppresses liver cancer by inducing apoptosis and eliciting potent antitumor immunity.Oncol Rep. 2018 Dec;40(6):3447-3457. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6740. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30272318 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Complex I Activity Is Required for Maximal Autophagy.Cell Rep. 2018 Aug 28;24(9):2404-2417.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.101. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30157433 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Syntaxin 17 by TBK1 Controls Autophagy Initiation.Dev Cell. 2019 Apr 8;49(1):130-144.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.01.027. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Dev Cell. 2019. PMID: 30827897 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK, a Regulator of Metabolism and Autophagy, Is Activated by Lysosomal Damage via a Novel Galectin-Directed Ubiquitin Signal Transduction System.Mol Cell. 2020 Mar 5;77(5):951-969.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.028. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 31995728 Free PMC article.
-
iRQC, a surveillance pathway for 40S ribosomal quality control during mRNA translation initiation.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 31;36(9):109642. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109642. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34469731 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

