TLR4 promotes the expression of HIF-1α by triggering reactive oxygen species in cervical cancer cells in vitro-implications for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 29207048
- PMCID: PMC5783462
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8108
TLR4 promotes the expression of HIF-1α by triggering reactive oxygen species in cervical cancer cells in vitro-implications for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
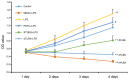
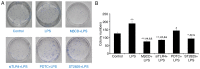
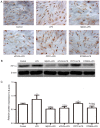
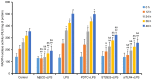
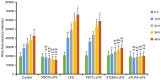
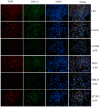
The present study investigated the mechanism underlying Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-mediated stimulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) activity and its association with reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cervical cancer cells. SiHa cells were cultured and randomized to control, lipopolysaccharide (LPS), methyl-β-cyclodextrin (MβCD)+LPS, ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate (PDTC)+LPS, ST2825+LPS and small interfering (si) RNA TLR4+LPS treatment groups. Cell proliferation was quantified using an MTT assay, cell cloning was performed using soft agar colony formation and HIF-1α expression was detected by immunocytochemical staining and western blot analyses. Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate and lucigenin luminescence assays were used to detect alterations in ROS and nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase content, respectively. Co-localization of TLR4 and HIF-1α was detected by immunofluorescence staining and observed using fluorescence microscopy. Compared with the control group, cell proliferation was enhanced in the LPS-treated group and was not altered in the PDTC+LPS treatment group. Cell proliferation was reduced in all other treatment groups (P<0.05). Compared with the LPS group, cell proliferation decreased in all other groups. Compared with the PDTC+LPS treatment group, cell proliferation significantly decreased when LPS was co-administered with ST2825, siTLR4 and MβCD (P<0.01). Treatment with MβCD+LPS exhibited an increased inhibitory effect on cell activity and proliferation. Compared with the control group, HIF-1α expression was enhanced following treatment with LPS, although it decreased when LPS was co-administered with ST2825, siTLR4 and MβCD (P<0.05). HIF-1α expression decreased following treatment with ST2825, siTLR4, MβCD and PDTC+LPS, compared with treatment with LPS alone. Compared with the PDTC+LPS group, HIF-1α activity decreased when LPS was co-administered with ST2825, siTLR4 and MβCD. NADPH oxidase and ROS levels increased in cells treated with LPS, compared with the control group, at 24 and 12 h following treatment, respectively, and decreased at 12 h when LPS was co-administered with ST2825, siTLR4 and MβCD. There was no difference between the LPS and PDTC+LPS groups with respect to NADPH and ROS levels. Compared with the PDTC+LPS group, NADPH oxidase activity and ROS content decreased when LPS was co-administered with ST2825, siTLR4 and MβCD. NADPH oxidase activity and ROS content were lowest in the MβCD+LPS treatment group, and immunofluorescent staining demonstrated that TLR4 was localized to the cell surface and HIF-1α was primarily localized to the cytoplasm. TLR4 was co-expressed with HIF-1α in cervical cancer cells. The results of the present study suggested that TLR4 signaling primarily promoted HIF-1α activity via activation of lipid rafts/NADPH oxidase redox signaling and may be associated with the initiation and progression of cervical cancer. This promoting effect was stronger in TLR4/lipid rafts/NADPH oxidase pathway than that in TLR4-NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, the TLR4/lipid raft-associated redox signal may be a target for therapeutic intervention to prevent the growth of cervical cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Soyasaponin Bb inhibits the recruitment of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) into lipid rafts and its signaling pathway by suppressing the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Jul;60(7):1532-43. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600015. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016. PMID: 27005845
-
Bilirubin inhibits the up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by scavenging reactive oxygen species generated by the toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:398-408. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26163808 Free PMC article.
-
[Hypoxia/reoxygenation and lipopolysaccharide induced nuclear factor-ΚB and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell injury and the interventional effect of emodin].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Jun;26(6):409-14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.06.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24912640 Chinese.
-
How does hypoxia inducible factor-1α participate in enhancing the glycolysis activity in cervical cancer?Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013 Jun;17(3):305-11. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23375385 Review.
-
MicroRNA Targeting Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidases in Cancer.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020 Feb 10;32(5):267-284. doi: 10.1089/ars.2019.7918. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020. PMID: 31656079 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipotoxicity and immunometabolism in ischemic acute kidney injury: current perspectives and future directions.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 23;15:1355674. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1355674. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38464721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ability of prebiotic polysaccharides to activate a HIF1α-antimicrobial peptide axis determines liver injury risk in zebrafish.Commun Biol. 2019 Jul 25;2:274. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0526-z. eCollection 2019. Commun Biol. 2019. PMID: 31372513 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of exosomes and microRNAs in HPV-mediated inflammation and cervical cancer: A review.Int J Cancer. 2020 Jan 15;146(2):305-320. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32688. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Int J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31566705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TLR4 mediates inflammation and hepatic fibrosis induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Aug;22(2):651-660. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11134. Epub 2020 May 7. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32626927 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol ameliorated endothelial injury of thoracic aorta in diabetic mice and Gly-LDL-induced HUVECs through inhibiting TLR4/HIF-1α.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun 10;25(13):6258-70. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16584. Online ahead of print. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34114347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wei KR, Chen WQ, Zhang SW, Zheng RS, Wang YN, Liang ZH. Epidemiology of uterine corpus cancer in some cancer registering areas of China from 2003–2007. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2012;47:445–451. (In Chinese) - PubMed
-
- Galli R, Starace D, Busà R, Angelini DF, Paone A, De Cesaris P, Filippini A, Sette C, Battistini L, Ziparo E, Riccioli A. TLR stimulation of prostate tumor cells induces chemokine-mediated recruitment of specific immune cell types. J Immunol. 2010;184:6658–6669. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902401. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

